ABI Model Pattern is a GUI library designed to initialize models, model properties, and also to define a set of rules for each property. The created models are necessary for storing the “structure” of data, restricting the integrity and ease of changing the conditions for their verification. All settings necessary for library operation are stored in a separate configuration file, the database is used only in the case of model binding to create a schema if necessary. The functionality for associating a model with a database will be described below.
 I was asked twice: “Tell me, Mr. Babbage, and if you enter the wrong data into the machine, will you get the right answer?” Incomprehensible is the confusion in the heads that leads to such questions.
I was asked twice: “Tell me, Mr. Babbage, and if you enter the wrong data into the machine, will you get the right answer?” Incomprehensible is the confusion in the heads that leads to such questions.
Charles Babbage, "Excerpts from the life of the philosopher" (1864)A graphical interface is needed to easily create models without additional study of the library logic, as well as to validate user actions during the definition of a set of rules for model properties, dynamically changing the creation form and displaying the corresponding errors. Logger and database connection settings.
To create a model in the library interface, it is necessary to define its properties and data verification conditions for these properties. The Validator class of the library compares the data of each input parameter with the conditions of the property of the specified model to form an Entity, and in the event of a discrepancy, terminates with a certain error.
The formed model (Entity) is an object with a consistent set of properties that stores the data transferred to create it. Each property can be mandatory and optional.
- Data for a required property must be passed in to form an entity;
- A non-mandatory property stores the data specified by default if the data for this property has not been transferred.
Since each Entity is an instance of the corresponding type, the instanceof operator can be used to verify that it belongs to the specified type.
Each model created is a new type that can be used to create the following model properties. A custom type can be used either as a property type or in a type collection. A simple example is the “Coupon” model as a type of property in the “Order” model.
Model "Coupon":

Model "Order":

A type collection can be used in the case of an unknown number of elements in an array or object. The data of each element of such a data structure must comply with the conditions of the created model, which is used as the property type. An example of a type collection can be considered as follows:
Shopping cart can store an unknown amount of products. In the model “Order” we add the property “Products” with the type “Array” and the collection of type “Product”. Each element of such a data structure must correspond to the type “Product”.
Model "Product":
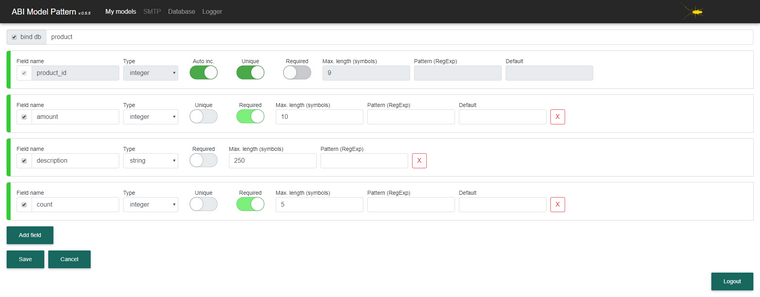
Model "Order":

To bind the model to the database, it is necessary to set the “bind_db” flag for each or individual properties on the Model Creation / Editing pages. The name of the table corresponds to the name of the model and the columns of this table correspond to the associated properties of the model, including the set of rules specified for them. The structure of related tables with models is changed if changes are made to the model.
An example of a related model "Order" in the database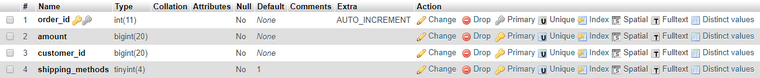
Before linking the model and its properties to the database, you need to configure the connection to the database in the library interface on the corresponding page.
In the current version of the library it is possible to use only MySQL database and a limited set of MySQL types.
This library has no functionality for writing Entity to the database, as well as deleting records. Creating such custom functionality, please note that when you change the properties of the model associated with the database, the structure of the table will change, and when you delete the model, the table will be deleted.
To use the logger, you must enable it and configure it in a separate page of the library interface.
Create models for all function parameters, data collections, queries, query responses, and other necessary parameters to validate the data. This is necessary to eliminate unexpected errors during the execution of the application and increase data control for their further processing.
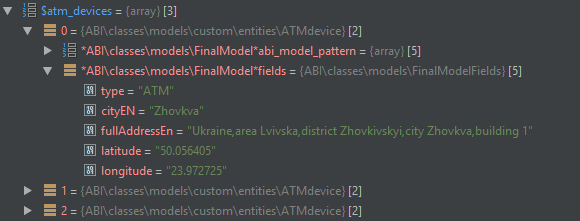
The Parser library class is required to iterate through the input parameters in the passed collection to create an Entity. Parser searches and finds in the transferred collection only those parameters that are needed to create an Entity. Parameter enumeration is not recursive. An example of receiving data in the private24 API and creating the ATM ATM entity.
Model "atm":

Model "atmdevice":
 Private24 API request URL:api.privatbank.ua/p24api/infrastructure?json&atm&address=&city=%D0%96%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0Private24 API response:
Private24 API request URL:api.privatbank.ua/p24api/infrastructure?json&atm&address=&city=%D0%96%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0Private24 API response:response{ "city":"", "address":"", "devices":[ { "type":"ATM", "cityRU":"", "cityUA":"", "cityEN":"Zhovkva", "fullAddressRu":", , , , , 1", "fullAddressUa":"i, i, i,i , i, 1", "fullAddressEn":"Ukraine,area Lvivska,district Zhovkivskyi,city Zhovkva,building 1", "placeRu":" \"\"", "placeUa":"i \"\"", "latitude":"50.056405", "longitude":"23.972725", "tw":{ "mon":"09:00 - 18:00", "tue":"09:00 - 18:00", "wed":"09:00 - 18:00", "thu":"09:00 - 18:00", "fri":"09:00 - 18:00", "sat":"09:00 - 16:00", "sun":"00:00 - 00:00", "hol":"00:00 - 00:00" } }, { "type":"ATM", "cityRU":"", "cityUA":"", "cityEN":"Zhovkva", "fullAddressRu":", , , , , 33", "fullAddressUa":"i, i, i,i , i, 33", "fullAddressEn":"Ukraine,area Lvivska,district Zhovkivskyi,city Zhovkva,building 33", "placeRu":" \"\"", "placeUa":" \"i\"", "latitude":"50.055840", "longitude":"23.981580", "tw":{ "mon":"09:00 - 18:00", "tue":"09:00 - 18:00", "wed":"09:00 - 18:00", "thu":"09:00 - 18:00", "fri":"09:00 - 18:00", "sat":"09:00 - 16:00", "sun":"00:00 - 00:00", "hol":"00:00 - 00:00" } } ] }
Entity creation: try {

$atm_devices = $available_atms->devices;
} catch (Exception $e) { $error_message = $e->getMessage(); }
Add a line to remove "devices" from the "$ request_body" variable by initiating one of the possible not appropriate answers:
unset($request_body->devices);
In the "devices" property of the ATM model created earlier, the "required" rule was established. Removing "devices" from "$ request_body", once again we create Entity and get the following error:

Last logged errors by the Logger class are added to the corresponding page in the interface. It looks like this:

Library installation
- Download the latest version of the library.
- Unzip the downloaded archive into the directory where you want to install the library.
- To install dependencies for this library, run the install command from the “abi” directory of the library - “composer install”
- Be sure to enable the Apache mod_rewrite module and check that your virtual host is configured with the AllowOverride parameter.
- Check and, if necessary, set the attributes for the library configuration file with read and write permission (0666).
- After installing the library, use the username - admin and password - admin to log in to the library's GUI.
→
Link to repositoryMany thanks for the help and support
denaikG