Nowadays, using classes is one of the most popular ways to structure software projects. This approach to programming is also used in JavaScript. Today we publish a translation of the 15th part of a series of materials on the JS ecosystem. This article focuses on different approaches to the implementation of classes in JavaScript, on the mechanisms of inheritance and transpilation. We begin with a story about how prototypes work and with analyzing various ways of imitating class-based inheritance in popular libraries. Next, we will talk about how, thanks to transpilation, you can write JS programs that use capabilities that are either missing from the language or, although they exist in the form of new standards or sentences that are at different stages of coordination, are not yet implemented in JS- engines. In particular, we will talk about Babel and TypeScript and ECMAScript 2015 classes. After that, we will examine several examples that demonstrate the features of the internal implementation of classes in the JS V8 engine.
[We advise you to read] Other 19 parts of the cycle Overview
In JavaScript, we constantly encounter objects, even when, seemingly, we work with primitive data types. For example, create a string literal:
const name = "SessionStack";
After this, we can immediately, referring to
name , call various methods of an object of type
String , to which the string literal we created will be automatically converted.
console.log(name.repeat(2)); // SessionStackSessionStack console.log(name.toLowerCase()); // sessionstack
Unlike other languages, in JavaScript, by creating a variable containing, for example, a string or number, we can, without carrying out an explicit conversion, work with this variable as if it was originally created using the keyword
new and the corresponding constructor. As a result, by automatically creating objects that encapsulate primitive values, you can work with such values as if they are objects, in particular, to refer to their methods and properties.
Another noteworthy fact regarding the JavaScript type system is that, for example, arrays are also objects. If you look at the output of the
typeof command called for an array, you can see that it reports that the entity being examined has the
object data type. As a result, it turns out that the indices of the elements of an array are just properties of a particular object. Therefore, when we refer to an array element by index, it comes down to working with the property of an object of type
Array and getting the value of this property. If we talk about how data is stored inside ordinary objects and arrays, then the following two constructions lead to the creation of almost identical data structures:
let names = ["SessionStack"]; let names = { "0": "SessionStack", "length": 1 }
As a result, access to the elements of the array and to the properties of the object is performed at the same speed. The author of this article says that he figured it out in the course of solving one complex problem. Namely, once he needed to carry out a serious optimization of a very important code fragment in a project. After he had tried many simple approaches, he decided to replace all the objects used in this code with arrays. In theory, access to array elements is faster than working with hash table keys. To his surprise, this replacement had no effect on performance, since both working with arrays and working with objects in JavaScript is reduced to interacting with the keys of the hash table, which in the other case requires the same amount of time.
Imitation of classes using prototypes
When we think about objects, the first thing that comes to mind is classes. Perhaps, each of those who are engaged in programming today created applications whose structure is based on classes and on the relationship between them. Although objects in JavaScript can be found literally everywhere, the language does not use the traditional class-based inheritance system. In JavaScript,
prototypes are used to solve similar problems.
Object and its prototypeIn JavaScript, each object is associated with another object - with its prototype. When you try to access a property or method of an object, the search for what you need is first performed in the object itself. If the search was not successful, it continues in the prototype of the object.
Consider a simple example that describes the constructor function for the base class
Component :
function Component(content) { this.content = content; } Component.prototype.render = function() { console.log(this.content); }
Here we assign the
render() function to the prototype method, since we need each instance of the
Component class to use this method. When, in any instance of
Component , the
render method is called, its search begins in the object for which it is called. Then the search continues in the prototype, where the system finds this method.
A prototype and two instances of the Component class.Let us now try to extend the
Component class. Create a new class constructor -
InputField :
function InputField(value) { this.content = `<input type="text" value="${value}" />`; }
If we need the
InputField class
InputField extend the functionality of the
Component class and be able to call its
render method, we need to change its prototype. When a method is invoked for an instance of a child class, it makes no sense to look for it in an empty prototype. We need to, during the search for this method, it be found in the
Component class. Therefore, we need to do the following:
InputField.prototype = Object.create(new Component());
Now, when working with an instance of the class
InputField and calling the method of the
Component class, this method will be found in the prototype of the
Component class. To implement the inheritance system, you need to connect the
InputField prototype to an instance of the
Component class. Many libraries use the
Object.setPrototypeOf () method to solve this problem.
Extending the capabilities of the Component class using the InputField classHowever, the above actions are not enough to implement a mechanism similar to traditional inheritance. Every time we expand a class, we need to do the following:
- Make the child class prototype an instance of the parent class.
- Call, in the constructor of the descendant class, the constructor of the parent class to ensure the correct initialization of the parent class.
- Provide a mechanism for calling methods of the parent class in situations where the child class overrides the parent method, but there is a need to call the original implementation of this method from the parent class.
As you can see, if a JS developer wants to take advantage of class-based inheritance, he will constantly have to perform the actions described above. In the event that you need to create a set of classes, all this can be arranged in the form of functions that are suitable for repeated use.
In fact, the task of organizing class-based inheritance was initially solved in the practice of JS development in this way. In particular, through various libraries. Such solutions have become very popular, which clearly indicated that something was clearly not enough in JavaScript. That is why ECMAScript 2015 introduced new syntactic constructions aimed at supporting work with classes and at implementing the corresponding inheritance mechanisms.
Class transpiltation
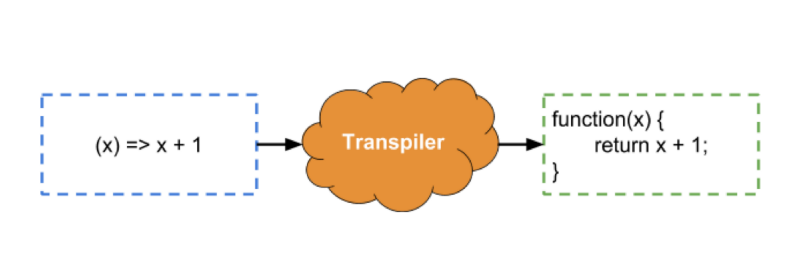
After the new features of ECMAScript 2015 (ES6) were proposed, the JS-developers community wanted to take advantage of them as soon as possible, without waiting for the end of the lengthy process of adding support for these features to JS engines and browsers. In solving such problems, transpilation shows itself well. In this case, the transfusion is reduced to the transformation of JS-code, written according to the rules of ES6, to a form that is understandable to browsers, which so far do not support the capabilities of ES6. As a result, for example, it becomes possible to declare classes and implement inheritance mechanisms based on classes, according to the ES6 rules, and transform these constructs into code that works in any browsers. Schematically, this process, by the example of processing the arrow function by the transpiler (another new language feature, which needs time to support), can be represented as shown in the figure below.
TranspilationOne of the most popular JavaScript transpilers is Babel.js. Let's see how it works by performing the transpilation of the code for the declaration of the
Component class, which we talked about above. So, here is the ES6 code:
class Component { constructor(content) { this.content = content; } render() { console.log(this.content) } } const component = new Component('SessionStack'); component.render();
But what this code turns into after transpilation:
var Component = function () { function Component(content) { _classCallCheck(this, Component); this.content = content; } _createClass(Component, [{ key: 'render', value: function render() { console.log(this.content); } }]); return Component; }();
As you can see, the output of the transpiler is ECMAScript 5-code, which can be run in any environment. In addition, there are added calls to some functions that are part of the standard library of Babel.
We are talking about the
_classCallCheck() and
_createClass() functions included in the transpiled code. The first function,
_classCallCheck() , is designed so that the constructor function is not called as a normal function. To do this, it checks whether the context in which the function is called is the context of an instance of the
Component class. The code checks whether the this keyword indicates a similar instance. The second function,
_createClass() , is responsible for creating object properties that are passed to it as an array of objects containing keys and their values.
In order to understand how inheritance works,
InputField analyze the class
InputField , which is the successor of the class
Component . Here is how class relationships are formed in ES6:
class InputField extends Component { constructor(value) { const content = `<input type="text" value="${value}" />`; super(content); } }
Here is the result of the transfiguration of this code with Babel:
var InputField = function (_Component) { _inherits(InputField, _Component); function InputField(value) { _classCallCheck(this, InputField); var content = '<input type="text" value="' + value + '" />'; return _possibleConstructorReturn(this, (InputField.__proto__ || Object.getPrototypeOf(InputField)).call(this, content)); } return InputField; }(Component);
In this example, the logic of the inheritance mechanisms is encapsulated in a call to the
_inherits() function. It performs the same actions that we described above, related, in particular, to writing an instance of the parent class to the prototype class.
In order to translate the code, Babel performs several transformations. To begin with, the ES6 code is parsed and converted into an intermediate representation, called an
abstract syntax tree . Then, the resulting abstract syntactic tree is transformed into another tree, each node of which is transformed into its ES5 equivalent. As a result, this tree is converted to JS-code.
Abstract syntax tree in Babel
An abstract syntax tree contains nodes, each of which has only one parent node. Babel has a base type for nodes. It contains information about what the node is and where it can be found in the code. There are different types of nodes, for example, nodes for representing literals, such as strings, numbers,
null values, and so on. In addition, there are nodes for representing expressions used to control the flow of program execution (
if construct), and nodes for loops (
for ,
while ). There is also a special type of node for representing classes. It is a descendant of the base class
Node . It extends this class by adding fields to store references to the base class and to the body of the class as a separate node.
Convert the following code snippet to an abstract syntax tree:
class Component { constructor(content) { this.content = content; } render() { console.log(this.content) } }
Here is what its schematic representation will look like.
Abstract syntax treeAfter creating a tree, each node is transformed into its corresponding node ES5, after which this new tree is converted into code that complies with ECMAScript 5. During the conversion process, first find the node that is farthest from the root node, after which this node is converted into code using snippets generated for each node. After this process is repeated. This technique is called
depth-first search .
In the above example, the code for two
MethodDefinition nodes will first be generated, then the code for the
ClassBody node will be generated, and finally the code for the
ClassDeclaration node.
TypeScript Transpilation
Another popular system that uses transpilation is TypeScript. This is a programming language, the code on which is transformed into ECMAScript 5 code, understandable to any JS engine. It offers new syntax for writing JS applications. Here's how to implement the
Component class in TypeScript:
class Component { content: string; constructor(content: string) { this.content = content; } render() { console.log(this.content) } }
Here is the abstract syntax tree for this code.
Abstract syntax treeTypeScript supports inheritance.
class InputField extends Component { constructor(value: string) { const content = `<input type="text" value="${value}" />`; super(content); } }
Here is what happens when you transpose this code:
var InputField = (function (_super) { __extends(InputField, _super); function InputField(value) { var _this = this; var content = "<input type=\"text\" value=\"" + value + "\" />"; _this = _super.call(this, content) || this; return _this; } return InputField; }(Component));
As you can see, we again have the ES5 code, in which, in addition to standard constructions, there are calls to some functions from the TypeScript library. The capabilities of the
__extends() function
__extends() similar to those we talked about at the very beginning of this material.
Thanks to the widespread use of Babel and TypeScript, the mechanisms for class declaration and class-based inheritance have become standard tools for structuring JS applications. This has contributed to adding support for these mechanisms to browsers.
Browser class support
Class support appeared in the Chrome browser in 2014. This allows the browser to work with class declarations without the use of transfiguration or any auxiliary libraries.
Working with classes in the Chrome JS consoleIn fact, browser support for these mechanisms is nothing more than “syntactic sugar”. These constructs are converted to the same basic structures that are already supported by the language. As a result, even if you use the new syntax, at a lower level, everything will look like the creation of constructors and manipulations with the prototypes of objects:
Class support is “syntactic sugar”V8 class support
Let's talk about how the support of ES6 classes in the V8 JS engine works. In the
previous article on abstract syntax trees, we said that when preparing a JS code for execution, the system produces its syntax analysis and forms an abstract syntax tree based on it. When parsing constructions of class declarations, nodes of type
ClassLiteral fall into an abstract syntactic tree.
In such sites are stored a couple of interesting things. Firstly, this is a constructor as a separate function, and secondly, it is a list of class properties. These can be methods, getters, setters, public or private fields. Such a node also keeps a reference to the parent class, which extends the class for which the node is formed, which, again, stores the constructor, the list of properties, and a link to its own parent class.
After the new
ClassLiteral node
ClassLiteral transformed into code , it is transformed into constructions consisting of functions and prototypes.
Results
The author of this material says that the
SessionStack company is
striving to optimize the code of its library as fully as possible, since it has to solve difficult tasks of collecting information about everything that happens on web pages. In the course of solving these problems, the library should not slow down the work of the analyzed page. Optimization of this level requires taking into account the smallest details of the JavaScript ecosystem affecting performance, in particular, taking into account the features of how classes and inheritance mechanisms in ES6 are arranged.
Dear readers! Do you use ES6 syntax to work with classes in javascript?
