Good time to read, dear users of Habr!
The proposed post proposes a tunnel modeling notation, originally described in the
Tunnel Modeling articles
- version 0.9 and
the Zachman Approach Transformation .
The basis of the approach is the Descartes dualism, for which a mathematical model is proposed in the form of two rotating hyperbolic surfaces — an abstract (above) and a material (below) (Fig. 1).
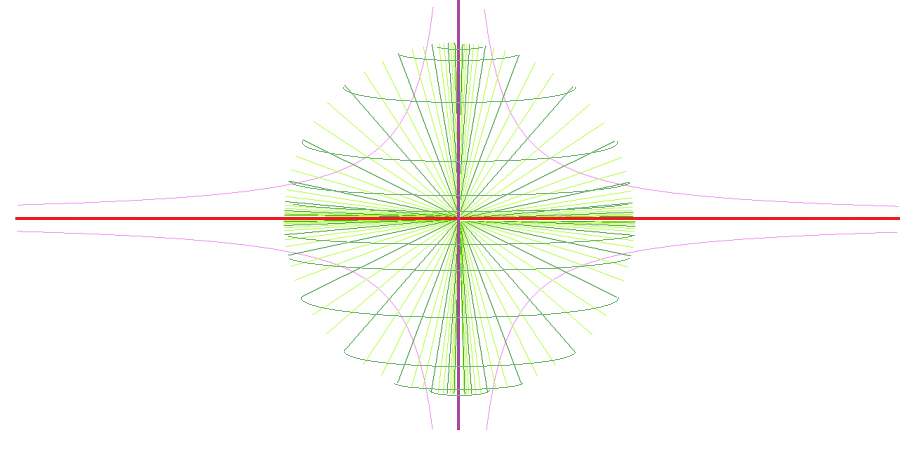 Fig. 1 Hyperbolic surfaces and spherical outlook
Fig. 1 Hyperbolic surfaces and spherical outlookIn the framework of the proposed model, it is assumed that the simplification of the abstract occurs infinitely up, the simplification of the material goes infinitely down, and the complication occurs infinitely when approaching the middle. Evaluation of the terms of the subject area is proposed to hold clusters for which the angle between the axis and the cone is determined by the formula
w =
arctan (1 / x 2 ) ,
x =
q n ,
where
q > 1 is the scale factor,
n is the integer number of the boundary between the clusters.
For definiteness, we will assume that for
n = 0 in the material there is a border between systems (biology) and processes (psychology). Similarly, in the field of the abstract, clusters of cultural and political science are separated.
We can suggest the following distribution of clusters by difficulty levels:
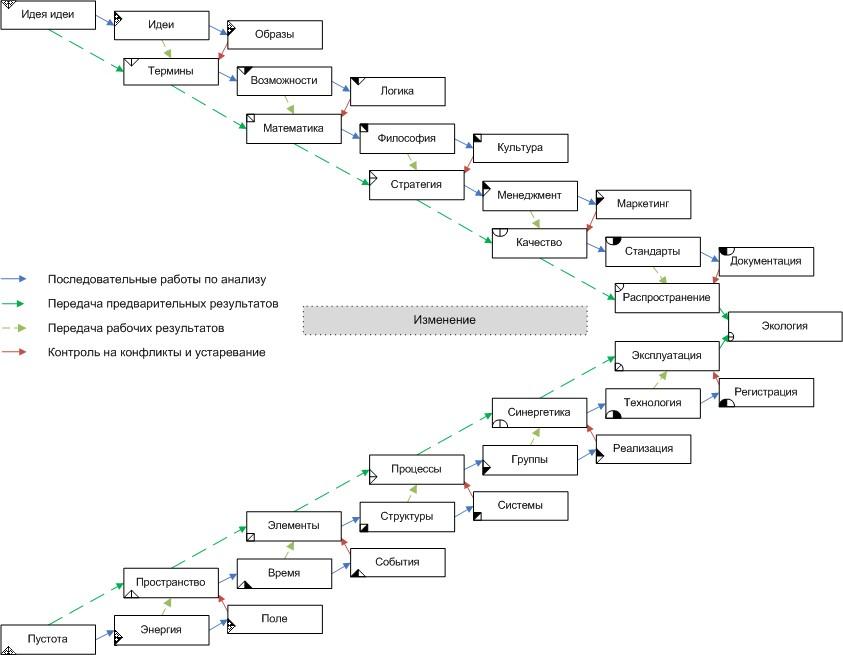 Fig.2 Division of the subject area by difficulty levels
Fig.2 Division of the subject area by difficulty levelsThis approach was used to analyze the terminology of the textbook of system-engineering thinking A.I. Levenchuk, in this case (with the introduction in the horizontal plane of division into phases of the quality management cycle), the following distribution was obtained:
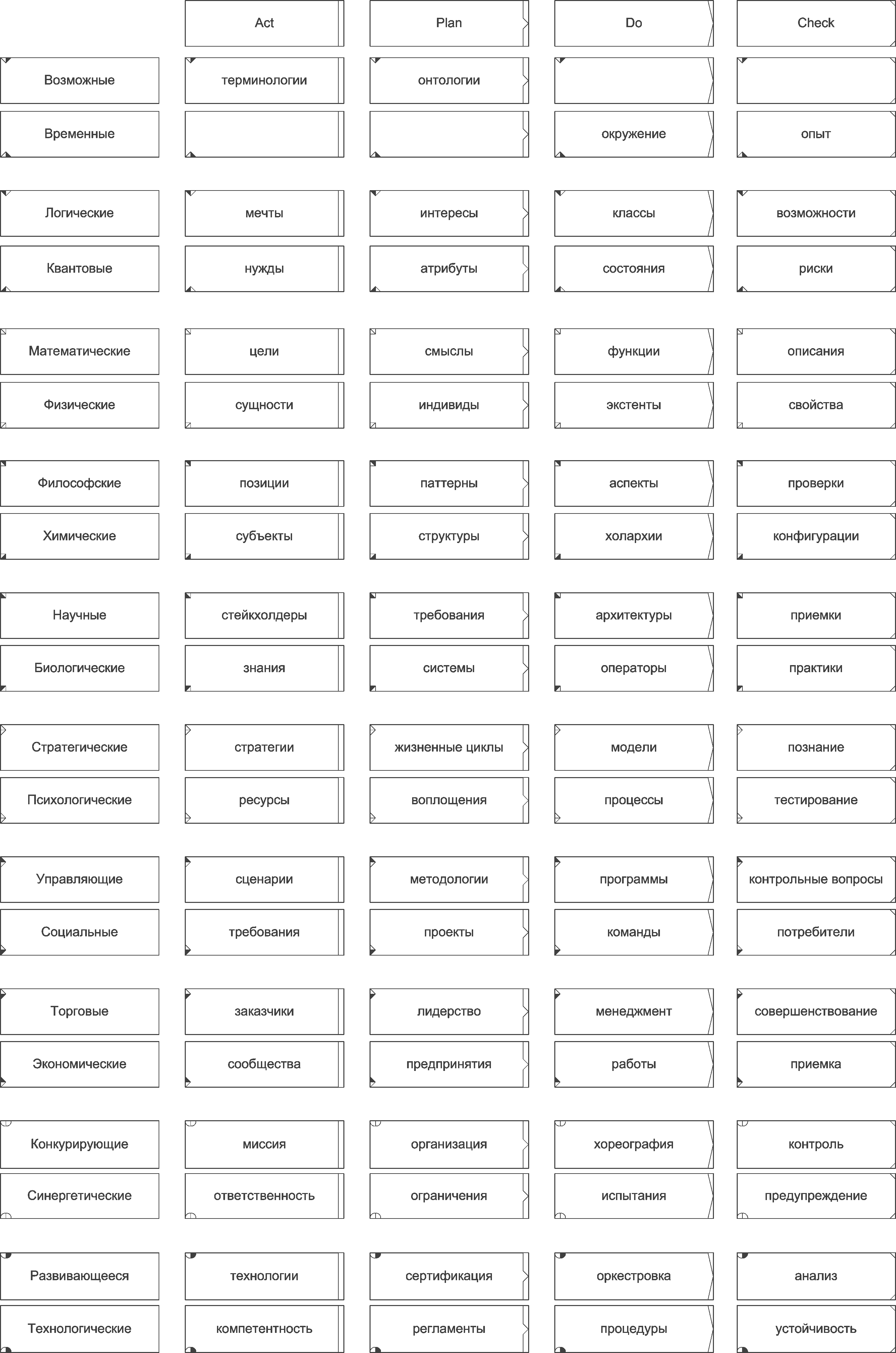 Fig.3 Proposal for the distribution of the terms of system-engineering thinking
Fig.3 Proposal for the distribution of the terms of system-engineering thinkingFor terms used in the
IDEF0 (SADT) methodology, the following abstraction chains and complications reflecting
the Deming-Shewhart cycle can be demonstrated:
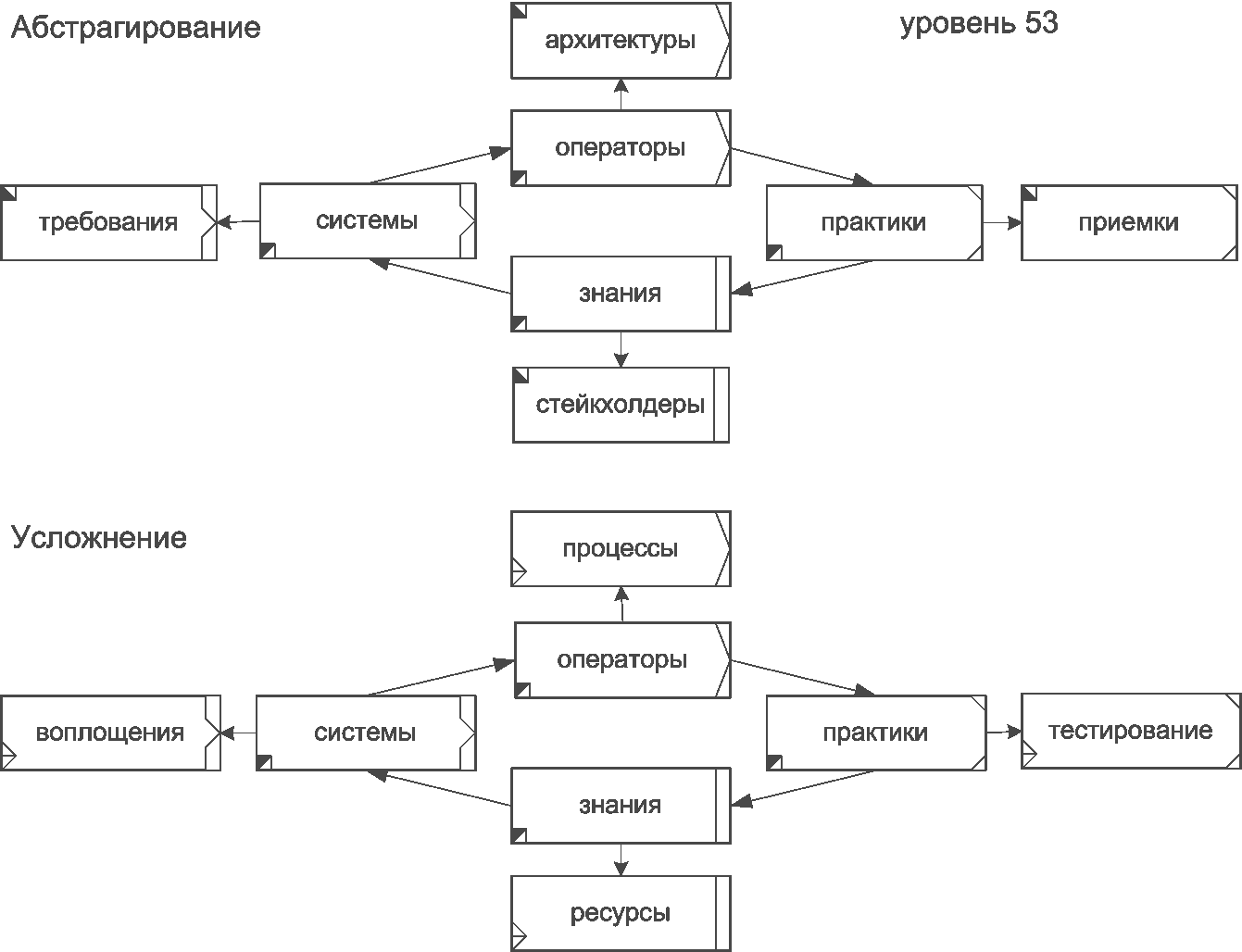 Fig.4 Abstraction and complication operations
Fig.4 Abstraction and complication operationsThe use of this set in the analysis of the subject area revealed its insufficiency in the description of the types of resources. In this regard, a separate set of images is proposed for resource types:
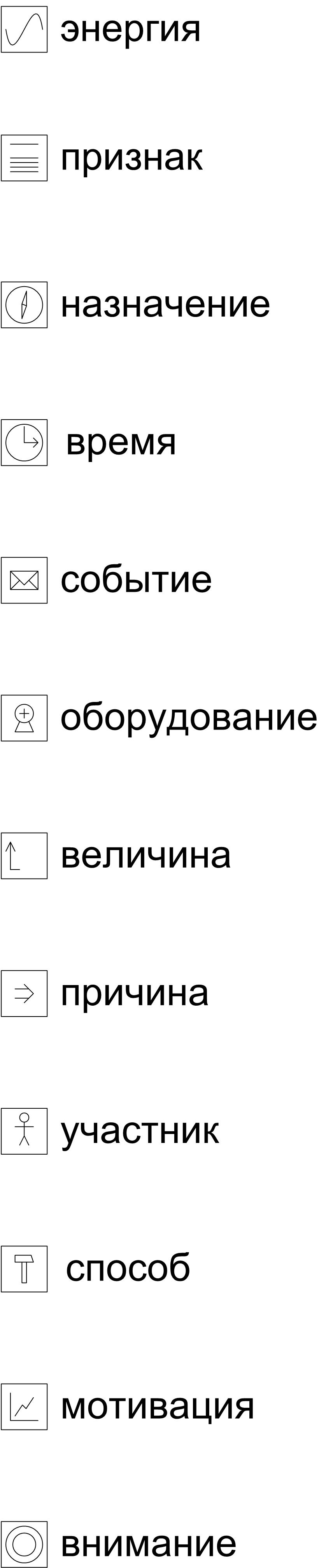 Fig.5 Designations for types of resources
Fig.5 Designations for types of resourcesThis set of graphic elements is no less expressive than
EPC , and has more regularity than
BPMN , which suggests the possibility of its use for modeling human-machine systems. The distribution of the levels of complexity was used in the analysis of the documentation of large projects.
I ask the participants to indicate the subject areas that are poorly covered by this approach.
PS Distribution by Levels and Resource Types
