This tutorial is about how to connect a USB camera to the Raspberry Pi or BeagleBone Blue and use it with ROS (Robot Operating System) - to read data from the camera via ROS image_view and even stream the video to a web browser!
At the end of the video demonstration on the robot EduMip.
1) As a bonus, we will create a distributed ROS system.
2) The Roscore application and the image viewer will work on the PC (master) and the camera node on the Raspberry Pi (slave).
3) To set up master and slave, we need to update the environment variables on both devices.
4) On the wizard: find the IP address of the device. For ethernet, net_dev can be either enpXXs0 or ethX:
$ ifconfig {net_dev} ifconfig enp61s0 ifconfig
5) Use the IP address as the value for the ROS_IP variable:
$ export ROS_IP="10.42.0.1"
6) And for ROS_MASTER_URI:
$ export ROS_MASTER_URI="http://10.42.0.1:11311"
7) If you want to use these values for future sessions, you can save the values in a .bashrc file in your home directory:
$ echo 'export ROS_IP="10.42.0.1"' >> ~/.bashrc $ echo 'export ROS_MASTER_URI="http://10.42.0.1:11311"' >> ~/.bashrc
8) Connect to the Raspberry Pi via ssh:
$ ssh {user}@{raspberry_ip}
9) For RPi as a slave device, add the main IP address for ROS_MASTER_URI
10) And the IP address of the Raspberry Pi for ROS_IP
$ export ROS_IP="10.42.0.65" $ export ROS_MASTER_URI="http://10.42.0.1:11311" $ echo 'export ROS_IP="10.42.0.65"' >> ~/.bashrc $ echo 'export ROS_MASTER_URI="http://10.42.0.1:11311"' >> ~/.bashrc
11) Now it's time to connect a USB camera.
12) Check if the camera is recognized by the system ::
$ lsusb $ ls /dev | grep video*
13) Install the node ROS usb_cam with the necessary dependencies:
$ sudo apt install ros-kinetic-usb-cam
14) The usb_cam node already has a test startup file:
$ cat /opt/ros/kinetic/share/usb_cam/launch/usb_cam-test.launch
15) Before launching this file, let's run the ROS kernel on master:
$ roscore
16) And now run the usb_cam node on the slave:
$ roslaunch usb_cam usb_cam-test.launch
17) Now we can see the topics created. We can check them either on the master or on the slave.
18) Put the current process in the background using CTRL + Z and execute the bg command to continue execution in the background. (on Ubuntu version not full desktop and no screen, just run another terminal)
19) To see the themes in the terminal:
$ rostopic list
20) ... or in the graphical interface:
$ rqt_graph
21) Reading camera data using image_view:
$ rosrun image_view image_view image:=/usb_cam/image_raw

22) Or using rqt_image_view
23) Move the background task to the fore:
$ fg
24) The latest experiment to date - streaming to the web
25) Installing a ROS web video server:
$ sudo apt install ros-kinetic-web-video-server
26) To do this correctly, create a catkin workspace for our custom startup file:
$ mkdir -p ~/rosvid_ws/src $ cd ~/rosvid_ws $ catkin_make $ source devel/setup.bash
27) Then create the ROS package:
$ cd src $ catkin_create_pkg vidsrv std_msgs rospy roscpp
28) Create a startup file using nano, vim, etc .:
$ mkdir -p vidsrv/launch $ nano vidsrv/launch/vidsrv.launch
place the
code there
from hereOn Beaglebone Blue with an A4Tech usb camera, I had this code:
<launch> <node name="usb_cam" pkg="usb_cam" type="usb_cam_node" output="screen" > <param name="video_device" value="/dev/video0" /> <param name="image_width" value="352" /> <param name="image_height" value="288" /> <param name="pixel_format" value="mjpeg" /> <param name="camera_frame_id" value="usb_cam" /> <param name="io_method" value="mmap"/> </node> <node name="web_video_server" pkg="web_video_server" type="web_video_server" \ /> </launch>
29) Assemble the package:
$ cd .. $ catkin_make
30) Run the ROS kernel on master again:
$ roscore
31) And run the generated startup file:
$ roslaunch vidsrv vidsrv.launch
32) The default web video server port is 8080
33) Open URL in web browser: {RPi_IP}: 8080
Links to documentation:
→
Video server node→
USB camera node→
rqt image viewer→
Raspberry Pi Camera Module nodeYou can use almost any USB camera that has drivers for linux; you can also use the Raspberry Pi Camera Module link above in the same way.
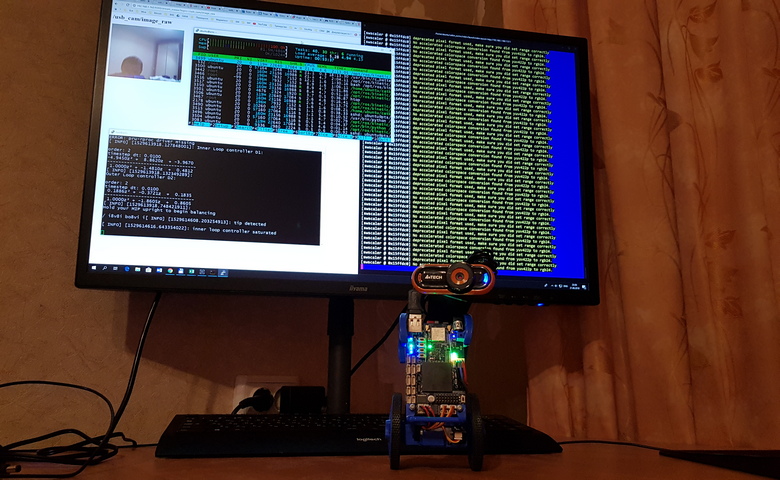
An example of how this works on BeagleBone Blue with an A4Tech camera:
Search for a three card for video from a USB camera BealeBone Blue (the recognition algorithm works on a laptop with master ROS).
