
When writing an article on the development of the anomaly detector, I implemented one of the algorithms called Incremental Growing Neural Gas.
AT Soviet literature In the Russian segment of the Internet, this topic is rather weakly covered, and only one article was found, and even then with the application of this algorithm.
So, what is the algorithm for incremental growing neural gas?
Introduction
IGNG, like GNG , is an adaptive clustering algorithm.
The algorithm itself is described in the article of Prudent and Ennaji for the year 2005 .
As with GNG, there are many data vectors. or generating function which provides vectors from arbitrarily distributed data (parameter - time or sample number in the sample).
Additional restrictions on the data algorithm does not impose.
But, inside is very different from GNG.
This algorithm is also curious by the fact that it is slightly more accurate than GNG models neurogenesis .
Algorithm Description
The algorithm breaks a lot of data into clusters.
Compared to GNG, its advantage is a higher rate of convergence.
The ideas on which the algorithm is based:
- Theory of adaptive resonance : “first, the nearest neuron is searched for, and if the difference does not exceed the threshold (“ vigilance parameter ”), the weights are corrected or, otherwise, the coordinate of the neuron is changed in the data space. If the threshold has not been overcome, new neurons are created, better approximating the value of the sample data.
- Both connections and neurons have an age parameter (in GNG, only connections), which is initially zero, but increases with learning.
- A neuron does not appear immediately: an embryo (or germinal neuron) first appears, whose age increases with each iteration until it matures. After training, only mature neurons participate in the classification .
Main loop
Work begins with a blank graph. Parameter initialized by the standard deviation of the training sample:
Where: - the average between the coordinates of the sample.
The main loop at each step decreases the value. which is the proximity threshold, and calculates the difference between the previous level of clustering quality and the level that was obtained after clustering by the IGNG procedure .
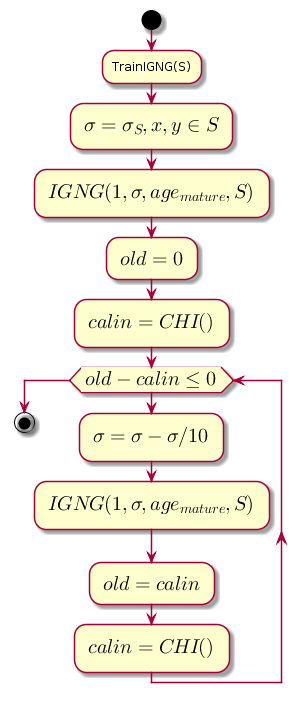
Chart code.@startuml start :TrainIGNG(S); :<latex>\sigma = \sigma_S,x,y \in S</latex>; :<latex>IGNG(1, \sigma, age_{mature}, S)</latex>; :<latex>old = 0</latex>; :<latex>calin = CHI()</latex>; while (<latex>old - calin \leq 0</latex>) :<latex>\sigma=\sigma - \sigma / 10</latex>; :<latex>IGNG(1, \sigma, age_{mature}, S)</latex>; :<latex>old = calin</latex>; :<latex>calin = CHI()</latex>; endwhile stop @enduml
CHI is the Kalinsky-Kharabaza index, showing the quality of clustering:
Where:
- - The number of data samples.
- - the number of clusters (in this case, the number of neurons).
- - matrix of internal dispersion (the sum of the squares of the distances between the coordinates of the neurons and the average for all data).
- - matrix of external dispersion (the sum of squares of the distance between all data and the nearest neuron).
The larger the index value, the better, because if the difference between the indices after clustering and before it is negative, it is possible to assume that the index became positive and exceeded the previous one, i.e. clustering completed successfully.
IGNG procedure
This is the basic procedure of the algorithm.
It is divided into three mutually exclusive stages:
- Neurons not found.
- Found one that satisfies the conditions of the neuron.
- Found two that satisfy the conditions of the neuron.
If one of the conditions passes, the other steps are not performed.
First, a neuron is searched for the best approaching sample data:
Here - the function of calculating the distance, which is usually the Euclidean metric .
If the neuron is not found, or it is too far from the data, i.e. does not meet the criterion of approximation A new embryonic neuron is created with coordinates equal to the coordinates of the sample in the data space.

If the proximity test has passed, the second neuron is searched in a similar way and its proximity to the data sample is checked.
If the second neuron is not found, it is created.

If two neurons were found that satisfy the condition of proximity to the data sample, their coordinates are corrected by the following formula:
Where:
- - adaptation step.
- - the number of the neuron.
- - Neuron Neighborhood Function with a neuron winner (in this case, it returns 1 for direct neighbors, 0 otherwise, because the adaptation step is for calculating will be nonzero only for direct neighbors).
In other words, the coordinate (weight) of the winning neuron changes to , and all its direct neighbors (those connected with it by one edge of the graph) on where - the coordinate of the corresponding neuron before the change.
Then a connection is created between the two winning neurons, and if it has already been created, its age will be reset.
The age of all other connections is increasing.
All connections whose age has exceeded a constant are deleted.
After that, all isolated (those that have no connection with others) mature neurons are removed.
The age of the immediate neurons-neighbors of the neuron-winner increases.
If the age of any of the germinal neurons exceeds , it becomes a mature neuron.
The final graph contains only mature neurons.
The condition for the completion of the IGNG procedure below may be considered a fixed number of cycles.
The algorithm is shown below (the picture is clickable):
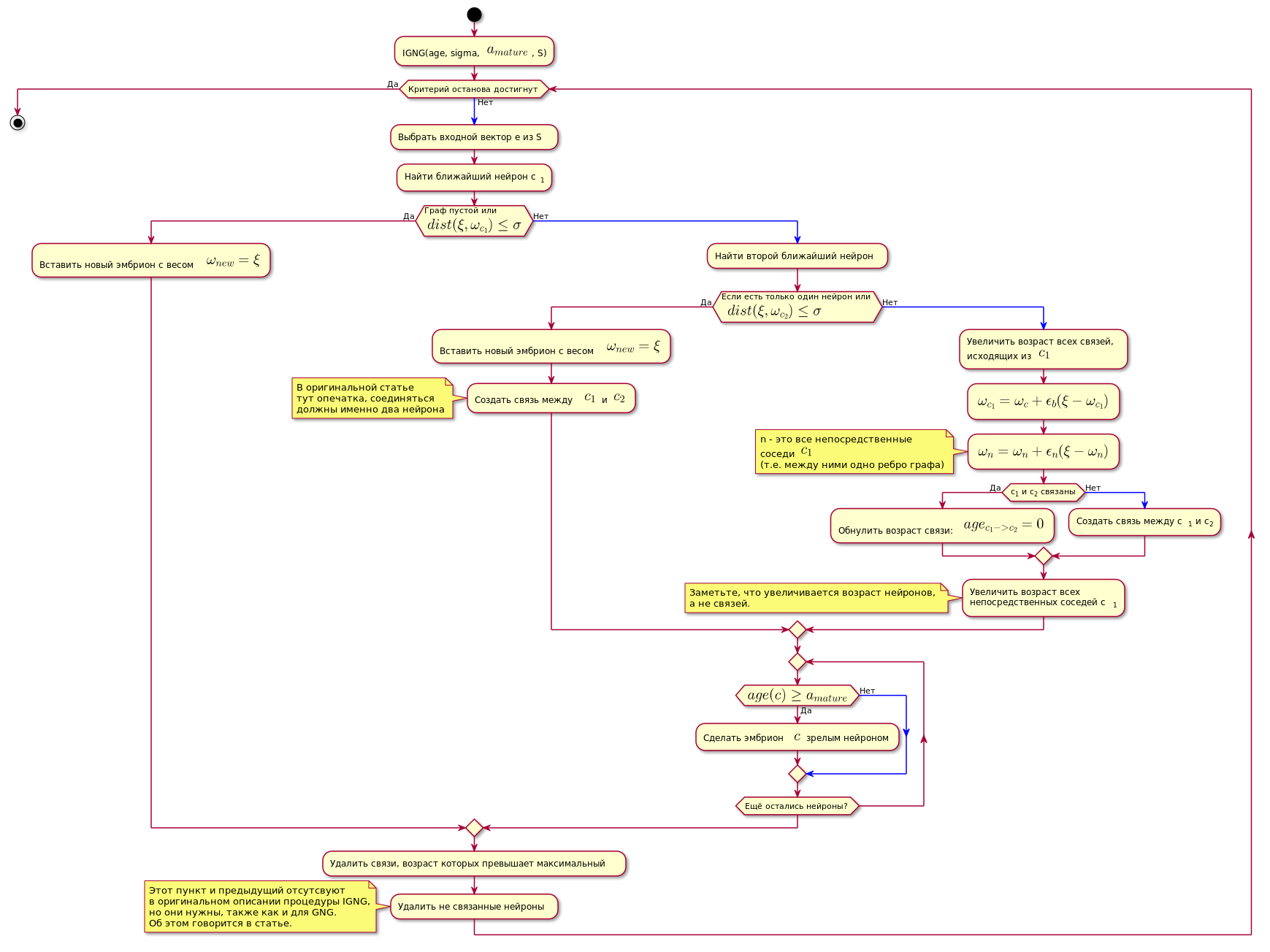
Chart code. @startuml skinparam nodesep 10 skinparam ranksep 20 start :IGNG(age, sigma, <latex>a_{mature}</latex>, S); while ( ) is () -[#blue]-> : e S; : c<sub>1</sub>; if ( \n<latex>dist(\xi, \omega_{c_1}) \leq \sigma</latex>) then () : <latex>\omega_{new} = \xi</latex>; else () -[#blue]-> : ; if ( \n <latex>dist(\xi, \omega_{c_2}) \leq \sigma</latex>) then () : <latex>\omega_{new} = \xi</latex>; : <latex>c_1</latex> <latex>c_2</latex>; note , end note else () -[#blue]-> : ,\n <latex>c_1</latex>; :<latex>\omega_{c_1} = \omega_c + \epsilon_b(\xi - \omega_{c_1})</latex>; :<latex>\omega_n = \omega_n + \epsilon_n(\xi - \omega_n)</latex>; note n - <latex>c_1</latex> (.. ) end note if (c<sub>1</sub> c<sub>2</sub> ) then () : : <latex>age_{c_1 -> c_2} = 0</latex>; else () -[#blue]-> : c<sub>1</sub> c<sub>2</sub>; endif : \n c<sub>1</sub>; note , , . end note endif repeat if (<latex>age(c) \geq a_{mature}</latex>) then () : $$ ; else () -[#blue]-> endif repeat while ( ?) endif : , ; : ; note IGNG, , GNG. . endnote endwhile () stop @enduml
Implementation
Network implementation is done in Python using the NetworkX graph library . Cutting out the code from the prototype in the previous article is given below. There is also a brief explanation of the code.
If someone is interested in the full code, here is the link to the repository .
Example of the algorithm:

Bulk code class NeuralGas(): __metaclass__ = ABCMeta def __init__(self, data, surface_graph=None, output_images_dir='images'): self._graph = nx.Graph() self._data = data self._surface_graph = surface_graph