
A few weeks ago, information security experts
warned of a dangerous malware known as VPNFilter. As it turned out, the main purpose of this malware are routers of various manufacturers. One of the first to get to VPNFilter was a team of information specialists
from Cisco Talos .
The malware is constantly being improved by developers. Recently, a new module was discovered that uses the
man-in-the-middle attack type against incoming traffic. Attackers can modify the traffic passing through the router. Also, they can easily redirect any data to their servers. The virus module is called ssler.
In addition to modifying incoming traffic, ssler can also transfer the victim’s personal data to its creators. These can be passwords for various resources, which cybercriminals then use for different purposes.
To prevent the theft of personal information, TLS encryption is usually used, which the malware can bypass. This is done by “downgrade” of HTTPS connections in HTTP traffic, which is not protected by anything. Then the request headers are replaced, which is a signal that the access point is vulnerable. Ssler specifically modifies the traffic of various resources, including Google, Facebook, Twitter and Youtube. The fact that these services provide additional protection. For example, Google redirects HTTP traffic to an HTTPS server. But the module allows you to bypass this protection, so that attackers receive unencrypted traffic.
Since the discovery of the virus, information security specialists
are exploring its capabilities . Now it turned out that it is more dangerous than it was thought. Previously, for example, Cisco experts argued that the main task of the attackers was infecting network devices in the offices of companies and the homes of the victims. Perhaps for the formation of a botnet. But now it turned out that it was the users, or rather, their data - the main goal.
“Initially, when we discovered a virus, we thought that it was created to implement various kinds of network attacks. But it turned out that this is not the main task and possibility of the malware. It was created mainly to steal user data and modify traffic. For example, a virus may change traffic in such a way that a client-bank user will see the same amount on his account. But in fact, there is no longer any money there, ”the report of cyber security experts says.
Interestingly, most of the infected devices are located on / in Ukraine. There are not too common defensive measures like
HTTP Strict Transport Security , so user data is at risk. But there are also problems in other countries - for example, in the USA and Western Europe many devices that are obsolete morally do not support working with HTTPS, while continuing to use HTTP.
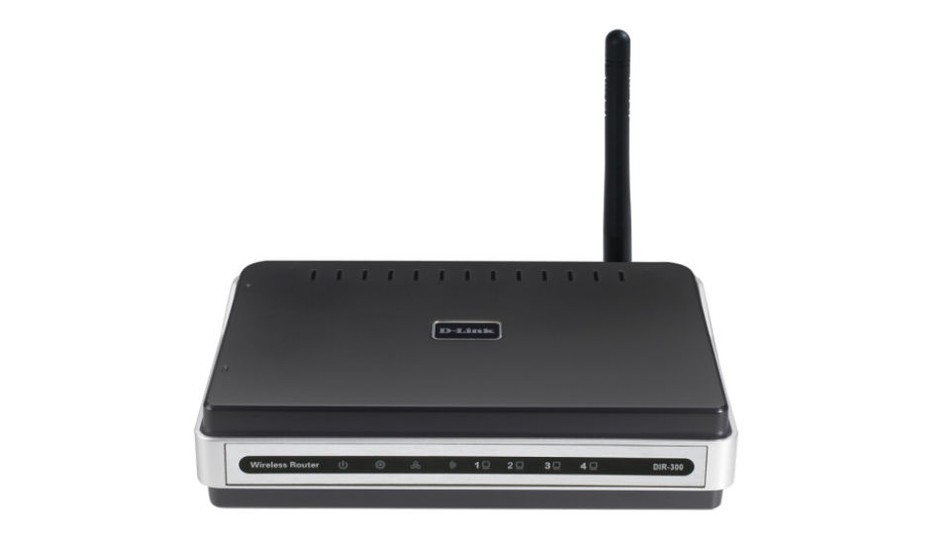
Earlier it was reported that the most vulnerable models of routers for this virus are devices manufactured by ASUS, D-Link, Huawei, Ubiquiti, UPVEL, and ZTE. In fact, the range of devices vulnerable to the virus is much wider. This, including models from Linksys, MikroTik, Netgear and TP-Link.
Full list of vulnerable devicesAsus:
RT-AC66U (new)
RT-N10 (new)
RT-N10E (new)
RT-N10U (new)
RT-N56U (new)
RT-N66U (new)
D-Link:
DES-1210-08P (new)
DIR-300 (new)
DIR-300A (new)
DSR-250N (new)
DSR-500N (new)
DSR-1000 (new)
DSR-1000N (new)
Huawei:
HG8245 (new)
Linksys:
E1200
E2500
E3000 (new)
E3200 (new)
E4200 (new)
RV082 (new)
WRVS4400N
Mikrotik:
CCR1009 (new)
CCR1016
CCR1036
CCR1072
CRS109 (new)
CRS112 (new)
CRS125 (new)
RB411 (new)
RB450 (new)
RB750 (new)
RB911 (new)
RB921 (new)
RB941 (new)
RB951 (new)
RB952 (new)
RB960 (new)
RB962 (new)
RB1100 (new)
RB1200 (new)
RB2011 (new)
RB3011 (new)
RB Groove (new)
RB Omnitik (new)
STX5 (new)
Netgear:
DG834 (new)
DGN1000 (new)
DGN2200
DGN3500 (new)
FVS318N (new)
MBRN3000 (new)
R6400
R7000
R8000
WNR1000
WNR2000
WNR2200 (new)
WNR4000 (new)
WNDR3700 (new)
WNDR4000 (new)
WNDR4300 (new)
WNDR4300-TN (new)
UTM50 (new)
QNAP:
TS251
TS439 Pro
Other QNAP NAS with QTS
TP-Link:
R600VPN
TL-WR741ND (new)
TL-WR841N (new)
Ubiquiti:
NSM2 (new)
PBE M5 (new)
Upvel:
Unknown Models * (new)
ZTE:
ZXHN H108N (new)
And that is not all
In addition to all that was announced above, in Talos reported the discovery of a sniffer module. It analyzes traffic in the search for data of a certain type, which are related to the operation of industrial systems. This traffic passes through TP-Link R600, which is determined by the module. In addition, the module looks for calls to IP from a certain range, as well as data packets whose size is 150 bytes or more.
“The creators of the virus are looking for very specific things. They are not trying to collect as much information as possible, not at all. They need passwords, logins, access to a specific range of IP and the like. We are trying to figure out who needs all this, ”the researchers say.
But that's not all, because now the virus is being updated, a self-destruct module has appeared in its functionality. When the module is activated, the virus is removed from the device without any traces.
Despite the fact that about a week ago the FBI discovered and seized the main server, the botnet still remains active, the measures taken were clearly not enough.