
It turns out that when the IT department of our customers estimates the cost of owning their own infrastructure, most of them forget to calculate, for example, electricity. Because the IT department pays the licenses and hardware, and the cold-power supply is generally the supply manager.
The total cost of ownership of physical equipment is a difficult thing, especially if you remember about the changing cost of money, purchases on credit and other parameters. Let me show you how we think and in which cases physical iron is better.
So, you usually need to compare the move to the cloud and the new rack, either at the time of the planned replacement of obsolete equipment, or at the time of creating a new infrastructure - for example, for a new project.
Let's go count.
The client is a large agricultural holding. Option 1 - own IT solution:
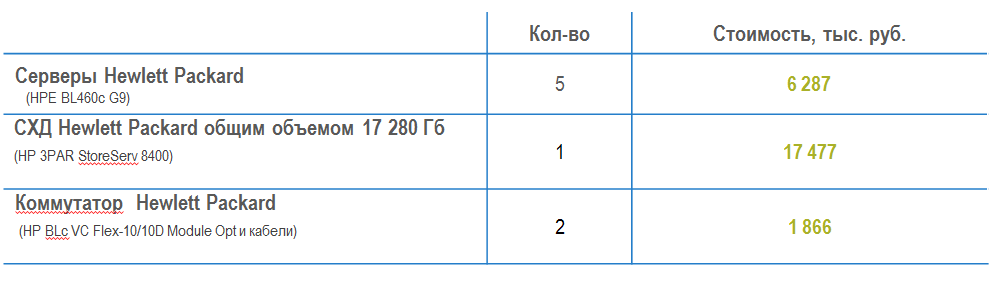
- Software and hardware infrastructure on Hewlett Packard hardware:
1. 5 HP 460c blade servers;
2. Storage with a total volume of 17 280 GB;
3. Switch - 2 pcs .;
4. Software for HP hardware performance and VMware virtualization. - The client has a discount from the vendor Hewlett Packard 25%.
- The client has its own server to host the equipment.
Option 2 - cloud service:
- VMware virtualization: vCPU - 325; RAM - 1 526 GB, HDD - 12 250 GB.
Now let's look at the numbers, and then discuss where and what are the pitfalls. In short, IT professionals need to be financially formed. In Russia, almost always the CIO is financially accountable. More precisely, it seems like they are equal in the structure of the company, but quite often CFO oversees CFO. And they may have misunderstandings and disagreements. As a result, all cases of IT specialists are checked by the financier. Why are financiers strange and often give illogical at first glance comments - it is always a question of an exact miscalculation.
Let's start with the results of these two models:

Now let's look at iron prices:
BY:
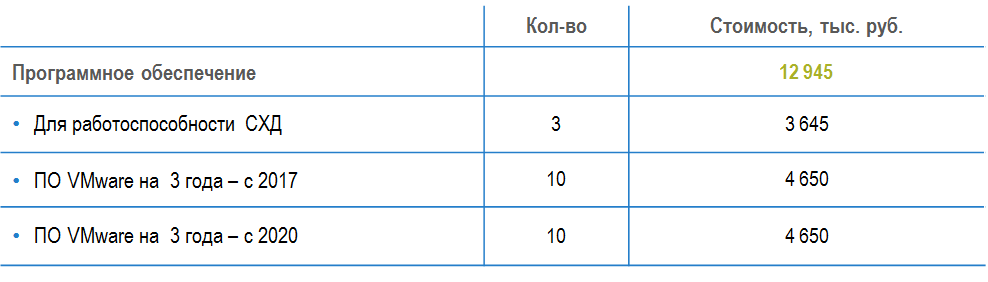
Operating cost:

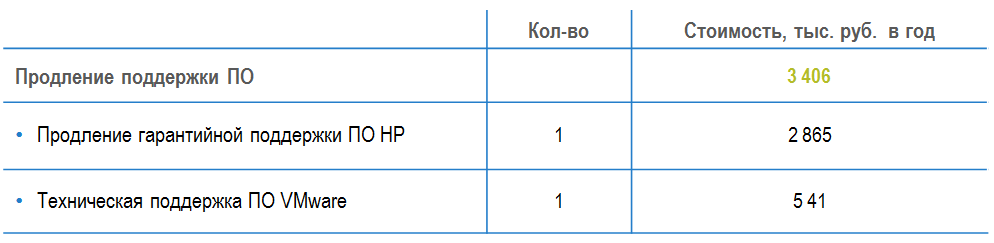
Expenses for software maintenance renewal:
It turns out that: the comparison was carried out over a five-year period.
To evaluate both options, we use the following indicator: Pure Discounted Cash Outflow (PED).
Why precisely he?
Because it can be directly compared with the KPI from the management cash flow statement. This allows you to assess the degree of its impact on business KPI.
And it saves us from having to request financial data from clients for each project.
The advantage of virtualization in the form of a gradual increase in leased resources is due to the fact that they are growing as needed. In this case, the planned launch of virtual capacity from 40% in the first year before reaching full capacity by the end of the third year. This approach allows constantly flexible approach to cost planning, which ensures maximum utilization of computing resources. While the purchase of equipment usually occurs in a volume that covers not so much the current needs (for a month or two in advance), but for a year or two in advance. Also, the ordered volume is increased to cover peak loads. Including an increase in the volume of purchases allows you to get certain discounts from suppliers.
PEDD is calculated as follows.
The amount of net cash outflow (MER) includes operating expenses (OPEX), residual value of investments at the end of the year, tax payments.
Next, we need to understand what the cost of the MER on the entire project is for 5 years today, i.e., to express it with the “current” amount. Since future money is always cheaper than today’s, we apply discounting of the BEP to adjust their value, as a result of which we get the Net Discounted Cash Outflow for the project as a whole over 5 years.
In our example, the NPT was calculated for both In-House and CLOUD, and the difference was 38.5 million rubles in favor of the cloud solution.
You can fairly note that purchased equipment can stand and work after 5 years. Although it is worth remembering that in 3 years it will be fully depreciated, technical support will become more expensive.
Also, the most practical of you will think that the purchased equipment is an asset and it can be sold, and to cover the investments made at the beginning of the project. And here it is important to understand that the sale is obtained not only with a very large discount (over 50%), but also stretches over the years.

A few more important things:
- When designing and purchasing your own hardware, there should be a reserve for high-availability clusters. It needs more equipment. The load on the system is usually calculated from the forecast of 1.5-2 years, then recycling gradually increases. And try to buy immediately, because there is a volume discount. Another additional iron is taken for seasonality, that is, under peak consumption.
In the cloud, you can flexibly vary the power and the redundancy is already there - VMs can move when specific hosts fail. On the other hand, if you have a geo-distributed cluster under critical processes, you will need a second cloud too. When using the cloud, it is possible to flexibly scale resources at the time of an increase in the seasonal load or to consume according to the Pay-as-you-go model. You can create machines, manage them, then delete them when the need is gone. We have postpay, quantization by the hour - but conditions may vary. You can use the service on a different pricing model and get a fixed pool of resources with a fixed monthly payment. Convenient for planning costs for future periods. - A server room is either an extension of the office, or a stand rental in a data center (at the provider’s site). Accordingly, this is also an expense.
- Rarely correctly considered the exploitation, specifically the wage fund (salary). The manager may decide that he will load his existing employees - and he will not have to increase the payroll. Training in work with new hardware and software and additional specialists are not taken into account. And each new person has a ratio of about two to three (up to five in Western companies) from his salary. These are taxes, contributions to funds, voluntary medical insurance, cellular communications, workplace costs (stationery, computer), office space (a piece of space rental), a piece of staff salaries such as office managers, cleaners and internal IT.
- Cooling, fire safety - this does not concern IT directly, but constitutes its cost item, this is understood by the CFO. The price of power supply is highly dependent on the consumer. A kilowatt comes to an office on average more expensive than to a factory or a data center.
- Not only servers and storage, but also network components are depreciated. A normal server has a depreciation period of 3 years, at a switchboard - 5 years. After that, the equipment must be changed, during this period the number of failures increases, the need for repairs increases. Equipment not only produces its own resource, but also simply becomes obsolete. We are guaranteed to change all network hardware once every 5 years, duplicate it according to the 2N scheme, and in the server park we always have a reserve of 30% for peaks.
- In the above calculation, the customer chose a comparison with HP servers, since he had experience in their operation. It is clear that you can choose a much cheaper Chinese nouneym, but then this will lead to less functionality of the equipment, suffering during its installation and operation, and often also to the lack of normal technical documentation. You can take iron at all without support or support with a weakened SLA, but this is also the risk of downtime and loss. You can also lay the license, it is an old Russian tradition.
- In the cloud, you can rent Microsoft licenses (or software services) and not purchase licenses for years to come, but pay for actual usage monthly. And you can transfer some of your own Microsoft licenses and not incur additional costs if the provider has a signed Mobility license agreement.
- Cost of money - equipment can be borrowed, leased, or under the HP program for large purchases with varying amounts of equipment from year to year. HP's terms and conditions were less profitable to the customer than other tools. Payment of iron is carried out in dollars or euros, which imposes additional risks. Therefore, when evaluating, a separate meeting with the financier is needed: all cash flows in the calculations are discounted to account for the time value of money. If you stop at the hardware, you need a contract with a vendor to fix the dollar or hedge risks. It is necessary to take into account inflation. Another inhouse loan is when one company in a group of companies gives money to another. If conditions are divine, this can be a very profitable option in favor of iron with an OPEX cost model.
- Old equipment can be sold, but due to the fact that the sale of IT equipment is usually not the main activity of the enterprise, and also because of the usually low demand for outdated and old equipment, possible restrictions on payment by non-cash method and other inconveniences, sell equipment it is possible with a very large discount, not everything and the process is stretched for months or even years.
When is iron more profitable?
When you immediately dispose of it by at least 80%, when you have a cheap loan within the group of companies and when you already have unused infrastructure that needs to be disposed of - for example, the network is idle, the storage controller will pull all necessary storage volumes in reserve, and its own IT staff drinks tea and smokes 8–10 times a day.
If you need such a calculation for your configuration, we can do. Free, but with malicious intent, of course: after such comparisons, new clients often come to our cloud. Sometimes not immediately, but after six months. Of course, we can explain all the terms and calculations that we do not understand now, and also show how they can influence the final results. If necessary, write to ESinegubkina@technoserv.com.