Ruthenium (Ru) - the fourth element with ferromagnetic properties at room temperature

With the periodic table, we are familiar from school. With years of research and research, new elements have appeared in it. But even those that have long occupied their honorable place in the table can demonstrate something new. Researchers from the University of Minnesota were able to prove that the chemical element number 44 - ruthenium - has very remarkable magnetic properties. How important is this discovery to the world of science and technology? How did you manage to discover the hidden properties of an already known element? And why were these searches originally organized? We will try to find answers to these questions. Go.
What is Ru?To get started is to get acquainted with the main character "person" of this event, with ruthenium. This is an element of the eighth group of the fifth period under atomic number 44. It is the so-called transition metal. In atoms of such elements, electrons appear on f and d
orbitals * .
The atomic orbital * is a one-electron psi function (in quantum mechanics it describes the pure state of the system), obtained as a result of solving the Schrödinger equation for a particular atom.
 The image shows the shapes and location in space of the f (green) and d (blue) orbitals.
The image shows the shapes and location in space of the f (green) and d (blue) orbitals.When talking about orbitals, letters are used that correspond to a certain value of the orbital quantum number, which determines the
kinetic (orbital) moment * of the electron.
Kinetic (orbital) moment * is a quantity that describes rotational motion, that is, a combination of such nuances: the mass of a rotating body, the distribution of mass relative to the axis of rotation, the speed of rotation.
The world first learned about the existence of ruthenium back in 1844 thanks to Karl Klaus, a professor at Kazan University. The name of this element is very patriotic, since the word “
Ruthenia ”, taken as a basis, translated from Latin means “
Russia ” or “
Russia ”.
To obtain ruthenium, it is necessary to
refine * platinum or other platinum metals.
Refining * - cleaning of heavy metals from impurities. In the case of platinum, this is purification by dissolving it in mineral acids and separating it from solution using reagents.
What is the new "told" ruthenium?The fact that some substances have magnetic, or rather ferromagnetic properties, mankind has known for quite some time. Until the last moment, only 3 elements from the periodic table were known, which are called ferromagnets at room temperature: nickel (Ni), iron (Fe) and cobalt (Co).
However, new research has shown that this short list will be a little longer. Ruthenium showed saturation of 148 emu / cm
-3 magnetization at room temperature and 160 emu / cm
-3 at 10 K (-263.15 ° C). It was also found that these magnetic properties begin to change with increasing thickness of the tested ruthenium film. The thicker the film, the weaker the magnetization.
Creating samples for researchRuthenium films 2.5, 6 and 12 nm thick were grown on an Al
2 O
3 substrate in the direction (1120) with an additional layer of molybdenum (Mo) 20 nm thick. The deposition process was carried out at 8 points under ultrahigh vacuum conditions at a pressure of 10
-8 Torr at each point.
Torr * is another name for the unit of measurement “millimeter of mercury”. Received his name in honor of the Italian mathematician and physicist Evangelista Torricelli.
A sample 2.5 nm thick was grown at room temperature. And samples with a thickness of 6 and 12 nm were heated to 400 ° C during annealing.
Crystallography samplesHaving grown a layer of molybdenum (20 nm) and ruthenium (2.5 nm) at room temperature, a control sample was created. Also, as an additional control sample, at a temperature of 400 ° C, a layer (110) of molybdenum 20 nm in thickness was created on an Al
2 O
3 substrate, but without ruthenium.

The image above (
1a ) shows the epitaxy of crystallographic families of the (110) Al
2 O
3 // (110) Mo / (011) Ru planes.
Epitaxial * communication was confirmed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), rotating the sample 360 °.
Epitaxy * - the growth of one crystalline material on the surface of another at lower temperatures.

In image
1b , the 4-fold symmetry of the (110) Al
2 O
3 planes is clearly visible, and the rotation of the molybdenum crystallographic orientation by 35 ° from the substrate plane (001) is also observed.

Plots
1c show the results of a θ – 2θ diffraction scan for all four samples.
A sample grown at room temperature showed no signs of texturing. But the samples 2.5, 6 and 12 nm thick, grown at 400 ° , demonstrated strong texturing (110) of molybdenum.

The last plot in this set,
1d , shows the X-ray reflectivity of textured samples. The degree of roughness for each sample was detected: 0.21 nm for the sample 2.5 nm thick, 0.13 for 6 nm and 0.21 for 6 nm thick.
 PREM photos
PREM photosThe images obtained by PREM (a transmission raster electron microscope) showed strong texturing of the molybdenum and ruthenium layers. A distortion of ruthenium epitaxy is also noted, which manifests itself in the form of (110) displacement of planes. Researchers believe that such a distortion is due to the mismatch of (001) molybdenum and (100) ruthenium.
Magnetic propertiesUsing a
vibration magnetometer * ,
hysteresis loops * (MH) were measured for ruthenium films grown at high temperatures, 2.5, 6 and 12 nm thick. Measurements were made at a temperature of 10 K and 300 K.
Vibration magnetometer * is a highly sensitive instrument for determining the magnetic properties of various magnetic materials.
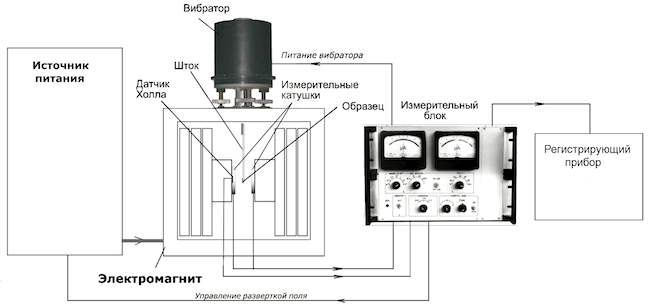 The scheme of measurements using a vibration magnetometer.
The scheme of measurements using a vibration magnetometer.The hysteresis loop * is a curve depicting the course of the dependence of the magnetization on the strength of the external field. The loop area displays the forces required for magnetization reversal.
For the 2.5 nm sample, measurements showed pronounced ferromagnetic properties. M
s at a temperature of 10 K was 160 emu / cm
-3 , and at a temperature of 300 K - 148 emu / cm
-3 . Since the calculations of M
s were carried out taking into account the fact that the entire area of the ruthenium film is magnetic, the relationship between the film thickness and the magnetization force was revealed. The thicker the film, the weaker the magnetization.
| Sub \ Mo (20) \ Ru (X) Sample | 2.5 nm | 6 nm | 12 nm | Control sample | Total for all samples |
|---|
| Made | five | five | 2 | five | 12 |
| FM | four | five | 2 | 0 | eleven |
| FM M vs. H | thirty | 21 | four | five | 55 |
Vibration Magnetometer Measurement Indicators:
- Made - the number of manufactured samples;
- FM is the number of samples demonstrating ferromagnetic properties;
- FM M vs. H is the number of hysteresis loops.
As can be seen from the table, samples with a thickness of 2.5 nm and 6 nm show similar results. Based on this, the average value of the magnetization for these samples was calculated (all samples of these thicknesses were taken into account in the calculations) - 141 emu / cm
-3 . The approximate value of the
coercive force * for all samples was 130 Oe (kA / m).
Coercive force * is an indicator of the magnetic field strength required for complete demagnetization of a ferromagnetic substance (or ferrimagnetic).
It was also necessary to exclude the possible "contamination" of the samples, that is, the possibility of an external influence of something on the sample, which could distort the measurement indicators. First of all, the sample holder was checked for this (the part of the measuring device where the sample is placed for fixation). After each measurement of each sample, the holder was checked for the presence of a paramagnetic signal. And to further clarify the results of the test, the measurements of the samples were made again using other holders.
Samples without crystallography were subjected to another check in order to confirm the fact that it was the textured ruthenium layer that was responsible for the manifestation of ferromagnetic characteristics. This test, fortunately for the researchers, was also successful.
The textured molybdenum sample grown on Al
2 O
3 at 400 ° C was also tested without applying a layer of ruthenium and showed no ferromagnetic properties. Thus, doubts were rejected regarding the fact that molybdenum or the heat treatment process could somehow “pollute” the tested samples, distorting the actual measurement results.
In order to measure the performance at the transition to room temperature, a sample with a thickness of 6 nm was used. The basis of this measurement was
the Hall resistance * , expressed by the function of the external field (Hz). For this,
the van der Pauw method * was used .
Hall effect * - the phenomenon of a transverse potential difference when placing a conductor with a constant current in a magnetic field.
The van der Pauw method * is a four-probe method for measuring the Hall coefficient. It is rather complicated in execution, since for its application certain conditions must be implemented:
- the sample should be flat and of uniform thickness, which should be less than its width and length;
- the sample must be homogeneous (homogeneous in composition);
- the sample must be isotopic (its physical properties must be identical over the entire area);
- All omnic contacts (between metal and semiconductor) must be located at the edges of the sample (or as close as possible to them);
- the area of each contact must be an order of magnitude smaller than the total area of the sample.

This graph is very indicative. We see the magnetoresistance (R
Hall ) and the Hall effect (H) for the textured (blue line) and non-textured (black line) Mo / Ru films. The Al
2 O
3 / Mo / Ru sample, which does not have a crystallographic texture, shows only an ordinary Hall effect. However, the textured pattern exhibits an abnormal Hall effect besides the usual one. Given that this sample does not have a perpendicular axis, the resistance will change as soon as the field is strong enough to cause saturation of the demagnetization field 4πM
s , where M
s is approximately equal to ~ 318 emu / cm
-3 .
The findings of researchers and future plansScientists took a long 2 years of hard work, which resulted in evidence that there are not only three elements in the world with ferromagnetic properties at room temperature.
Here is what Professor Wang, one of the project leaders, says:
It was exciting, but difficult. It took us 2 years to find the right way to grow this material and confirm its properties. This work will provoke all other researchers of magnetism to begin a search for the fundamental aspects of magnetism in well-known elements.
Intel quickly became interested in this research and wanted to further develop it. And not for nothing, because many scientists believe that the ability to manipulate the properties of substances at the atomic level is an incredibly important component of future discoveries that can start a revolution in various sectors of human life, in particular in the field of data storage and processing.
What was previously only a theory begins to take shape. And all this is happening thanks to the inquisitive minds of scientists who do not want to accept the world around them as their predecessors described it. Asking questions, wandering in search of truth, studying what, such as, has long been studied - the only way to achieve results. And the scientists of this project have achieved it.
I strongly recommend that you familiarize yourself with the original source and inspirer of this article - the report of scientistsAdditions to the research (graphs and tables) you can find on the link.Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends,
30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have
2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about
How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?