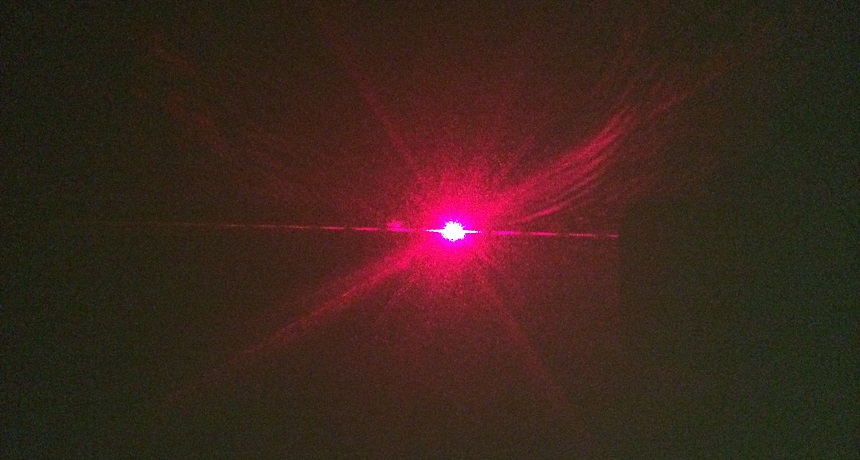
 This beautiful light shows a diffraction pattern of a laser beam illuminating human hair.
This beautiful light shows a diffraction pattern of a laser beam illuminating human hair.You can measure the thickness of a single hair at home. All you need is a dark room, a laser pointer, cardboard, duct tape and a bit of math. And, of course, someone's hair. For those who love educational videos - an article based on the
video from the Frosbite Theater .
1. It is necessary to make a small cardboard frame on which to place the hair. I cut a square with a side of about 15 cm out of cardboard, and then cut a small rectangle with sides of about 1x4 cm in its middle.
2. Take human hair — from your head, or from a volunteer's head. Make sure it is long enough so that it can be taped to both sides of the inner rectangle. In my case, the hair length should have been at least 5 cm, so that I could glue them at both ends.
3. Glue the hair as tightly as possible on both sides of the frame, so that the hair passes in the middle of the cut-out window.
4. In the dark room, stand farther than a meter away from the empty wall. Hold the frame with the hair in front of you and shine a laser pointer on the wall, placing the pointer just behind the hair, so that the light falls on it.
5. You will see how light scatters on both sides of the hair when you shine on it.
Hair causes diffraction of laser light. Diffraction is the bending of the path of a light wave passing near an object — with a human hair or through a slit in paper. Light can behave like a wave, and when it meets hair, it breaks into a pattern of repeating lines. This drawing can be seen on the wall. Its size is related to the size of the object that caused the scattering. This means that by measuring the size of the scattering, you can, using a bit of mathematics, find out the thickness of the hair.
6. Measure in centimeters the distance from your hair to the wall, on which the pointer shines.
7. Find out the wavelength of the light produced by the pointer. A red pointer will produce light with a wavelength of about 650 nm, and a green one about 532 nm. This is usually indicated on the pointer itself.
8. Measure the light scattering on the wall. It is necessary to measure the distance from the center point to the first visible dark band. It is necessary either to fix the pointer and the frame with the hair, or to ask someone to hold them during the measurements.
And now you have all the data you need to calculate the thickness of the hair. Make sure all your measurements are made in the same units. I, for example, got the following numbers:
- The distance between my hair and the wall is 187 cm.
- The laser wavelength is 650 nm, or 0.000065 cm.
- The average light scattering obtained by measuring seven hairs: 2.2 cm.
Then I substituted these values into the equation taken from the video:
In this equation, D is the diameter of the hair, m = scatter interval. I took measurements to the first dark band, so m = 1. λ is the laser wavelength, that is, 0.000065 cm. Sin θ is the scattering angle. It can be calculated by dividing the scattering measurement by the distance from the hair to the wall. In my case, this will be an average scatter of 2.2 cm divided by 187 cm.
In numerical form, the equation is:
And I got D = 0.005831 cm or 58 microns. The thickness of people's hair is usually in the range from 17 to 180 microns, and our hair perfectly fit into it, although it turned out to be a little thinner than the average.
Try it at home and share the results in the comments.
Keywords
Diffraction The curvature of the waves when meeting with the object. The pattern that the waves give out during diffraction can be used to determine the structure of small objects — for example, the thickness of a human hair.
Laser A device that creates a dense beam of coherent light of the same color. Lasers are used for making holes, cutting, leveling, as guides, as well as in surgery.
Physics Scientific study of the nature and properties of matter and energy.
Wavelength The distance between two peaks or dips of adjacent waves in a sequence. Visible light, which, like all electromagnetic radiation, is a wave, includes waves with a length of 380 nm (violet) to 740 nm (red). Radiation with shorter wavelengths than that of visible light is gamma rays, x-rays and ultraviolet. With large lengths - infrared light, microwaves and radio.