 Astronaut Jeffrey Hoffman removes the WFPC1 camera during a telescope upgrade. The photo was taken during the first mission of servicing the Hubble telescope, after which we were able to make one of the greatest photographs ever created by mankind, both in terms of science and in terms of aesthetics
Astronaut Jeffrey Hoffman removes the WFPC1 camera during a telescope upgrade. The photo was taken during the first mission of servicing the Hubble telescope, after which we were able to make one of the greatest photographs ever created by mankind, both in terms of science and in terms of aestheticsSince humankind first overcame the bonds of gravity and went beyond the atmosphere of our planet, we have been able to look at the Universe as we could not before. We were no longer limited by our location on Earth, and we didn’t necessarily have to deal with interference caused by an atmosphere several kilometers thick above us, as a result of which we discovered many cosmic truths that were inaccessible to us throughout the history of mankind. . Thanks to the breakthroughs in space travel, the ingenuity and investment of NASA, our scientific growth has been accompanied by the most stunning and interesting images ever received on Earth. Here are five images from NASA in five different areas that have changed our view of the world. [
Photo clickable / approx. trans. ]
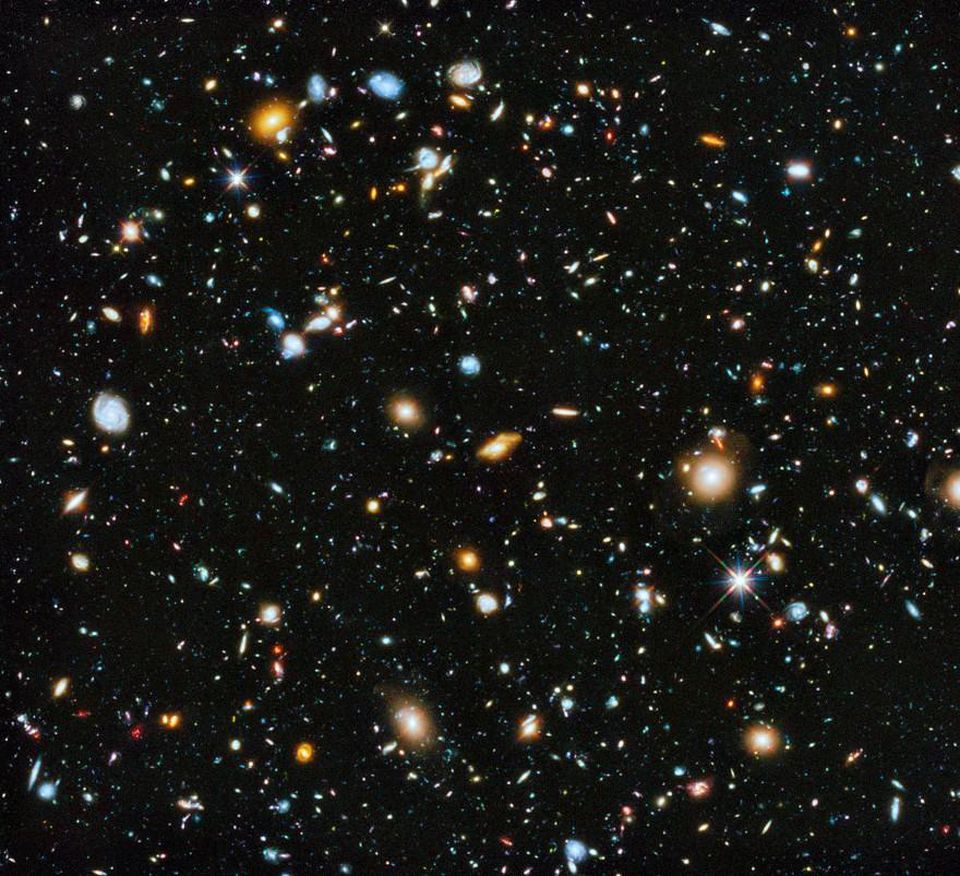 Composite image over ultraviolet, visible and infrared ranges from the Hubble eXtreme Deep Field experiment. The greatest of the images of the remote universe.
Composite image over ultraviolet, visible and infrared ranges from the Hubble eXtreme Deep Field experiment. The greatest of the images of the remote universe.1) Composite image of Hubble eXtreme Deep Field. Over 20 years ago, the first photo of Hubble Deep Field was taken. By directing the telescope to the black part of the sky, and collecting photons for several days in a row, we were able to discover what lies there, in the greatest cosmic abyss; billions and billions of galaxies. Since then, the Hubble telescope equipment has been updated many times, and thanks to it, we were able to use each photon much better, look deeper into the ultraviolet and infrared, increase the field of view and depth.
Image Extreme Deep Field (XDF) - the greatest of the photographs of the universe, which took 23 days of observation of the sky, which is only 1/32 000 000 of the entire sky. The experiment not only found more than five thousand galaxies, but also discovered amazing examples of the evolution of galaxies, since it was able to look back at the times when the age of the Universe was only 4% of the current one. We learned how the universe grew, how galaxies evolved from tiny structure beginnings to modern monsters. Most interestingly, we were able to make our first accurate estimate of the total number of galaxies in the observable universe: two trillion. Surprisingly, all this information is encrypted in a single image.
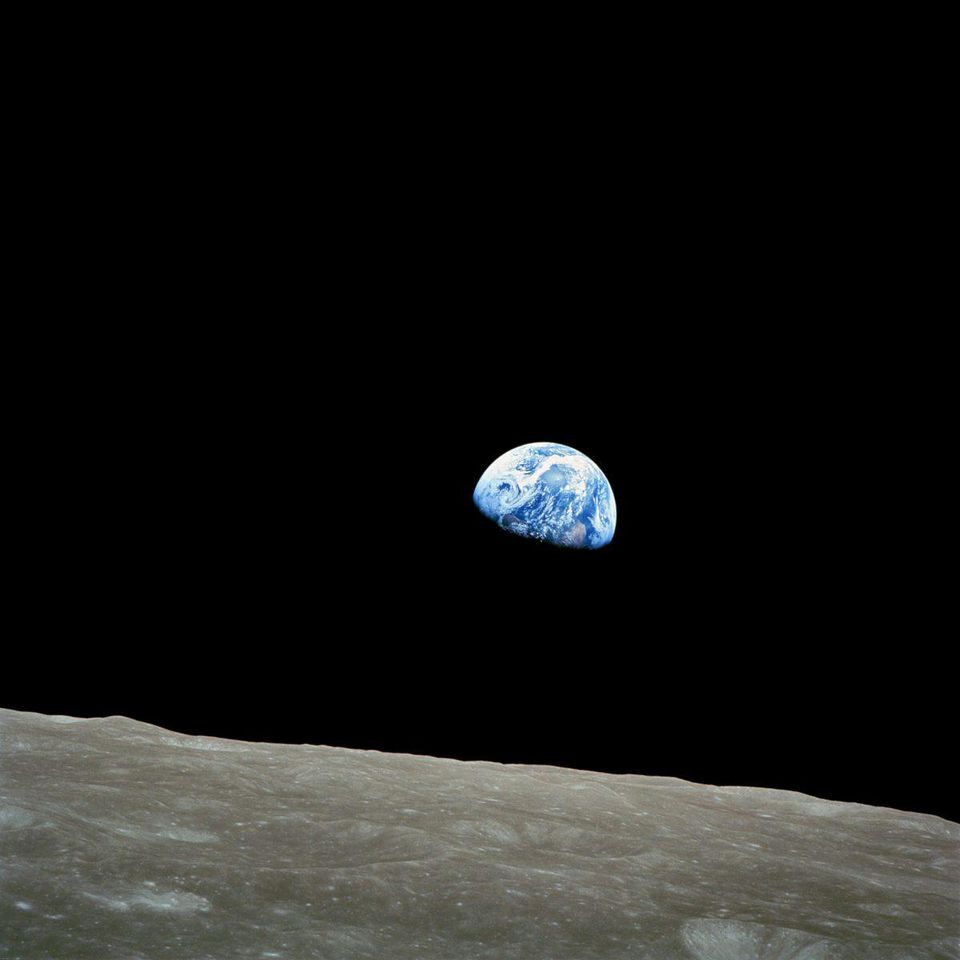 For the first time, human eyes saw the Earth rise above the Moon. This was probably the greatest moment of NASA that influenced education and public opinion before the first landing on the moon.
For the first time, human eyes saw the Earth rise above the Moon. This was probably the greatest moment of NASA that influenced education and public opinion before the first landing on the moon.2) Photo "Earth Rising" with Apollo-8. All information disclosed by NASA has always been aimed at training and working with the audience. The photo above is known under the simple name "Earth Rising", and this was the first time a person saw the Earth rise above the Moon. The photo was taken by astronaut Bill Anders during the completion of the Apollo-8 passage over the far surface of the Moon, and for the first time she showed humanity how unique, valuable, tiny and fragile the Earth was. Anders himself said the following:
We traveled a distance to explore the moon, and the most important discovery for us was the Earth.
The most interesting thing happened when Sister Mary Jasinda wrote a letter to NASA asking her to stop spending money on space exploration, while there was so much suffering on Earth. NASA's first assistant director of science,
Ernst Stalinger , responded with a long letter in which this photo was attached. There, in particular, it was said:
The picture I put in the letter shows a view of our Earth from Apollo 8 when it was in orbit around the moon on the Christmas of 1968. Of all the amazing results of the space program, this image is perhaps the most important. It opened our eyes to the fact that our Earth is a beautiful and most precious island in endless emptiness, and that for our life there is no other place than the surface layer of our planet bounded by the joyless emptiness of the cosmos. Never before have so many people realized how limited our Earth is and how dangerous it would be to disturb its ecological balance. From the moment of publication of this photo, voices warning of deadly problems confronting man in our time are becoming ever louder: environmental pollution, hunger, poverty, urban life, food production, water quality control, overpopulation. Obviously, it is not by chance that we are starting to notice the immense tasks facing us at the time when the young space age provided us with a first good look at our own planet.
We are very fortunate that the space age not only gave us a mirror in which we can see ourselves, but also provided us with the technologies, tasks, motivation and optimism to attack these tasks with confidence. What we learn from our space program fully supports what Albert Schweitzer meant when he said: “I look to the future with caution, but with hope.”
Like millions of other people, Jasinda changed her mind. With this photo, we can confidently answer the question of why investment in science is so important, despite all the suffering that exists in the world. All for the next generation to not have to endure the suffering that affects us today.
 The discovery of fluctuations in the residual glow of the Big Bang on scales smaller than 1 degree was the greatest achievement of the WMAP project, and it showed us the first accurate image of the “infant photo” of the Universe
The discovery of fluctuations in the residual glow of the Big Bang on scales smaller than 1 degree was the greatest achievement of the WMAP project, and it showed us the first accurate image of the “infant photo” of the Universe3) "Infant Photo of the Universe" by WMAP. One of the greatest discoveries of the 20th century was the residual glow of the Big Bang - relic radiation. The Big Bang spawned the Universe filled with matter, anti-matter and radiation, and this radiation travels in a straight line and gets into our eyes since the first atoms formed. Today, this radiation is very cold, due to the expansion of the Universe, but when it was emitted, it had to climb out of the gravity wells determined by the regions with high and low density that existed at that time.
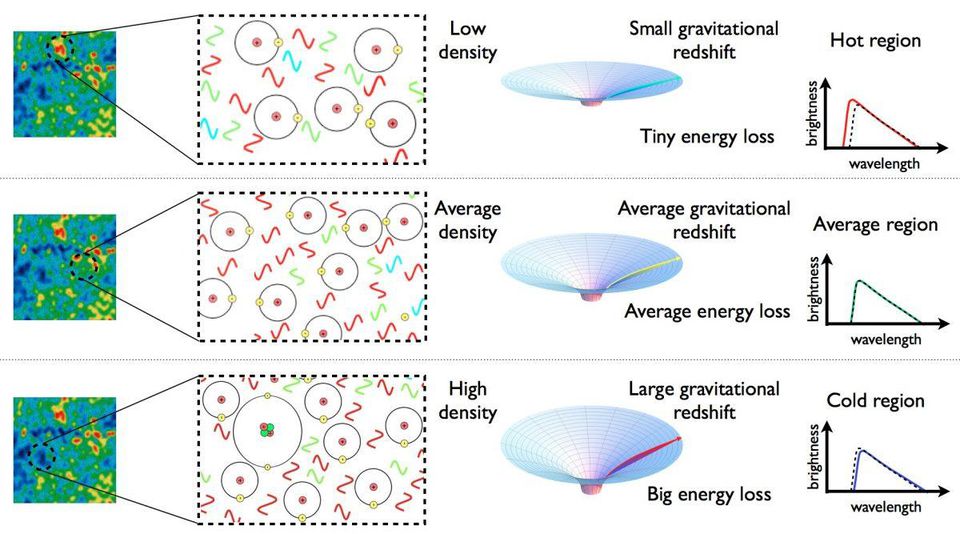 Regions with high, medium and low density that existed when the universe was only 380,000 years old now correspond to cold, medium and hot relict radiation.
Regions with high, medium and low density that existed when the universe was only 380,000 years old now correspond to cold, medium and hot relict radiation.These regions grew into galaxies, clusters, and cosmic
voids , but for the first time these details about the Universe with such detailing revealed the “infant photo” from WMAP. The amplitude and distribution of regions of low and high density look like temperature fluctuations in relic radiation, and tell us about what the universe consists of. The composition of the universe as a mixture of dark matter, normal matter and dark energy was first precisely determined by WMAP, and this changed our perception of the universe.
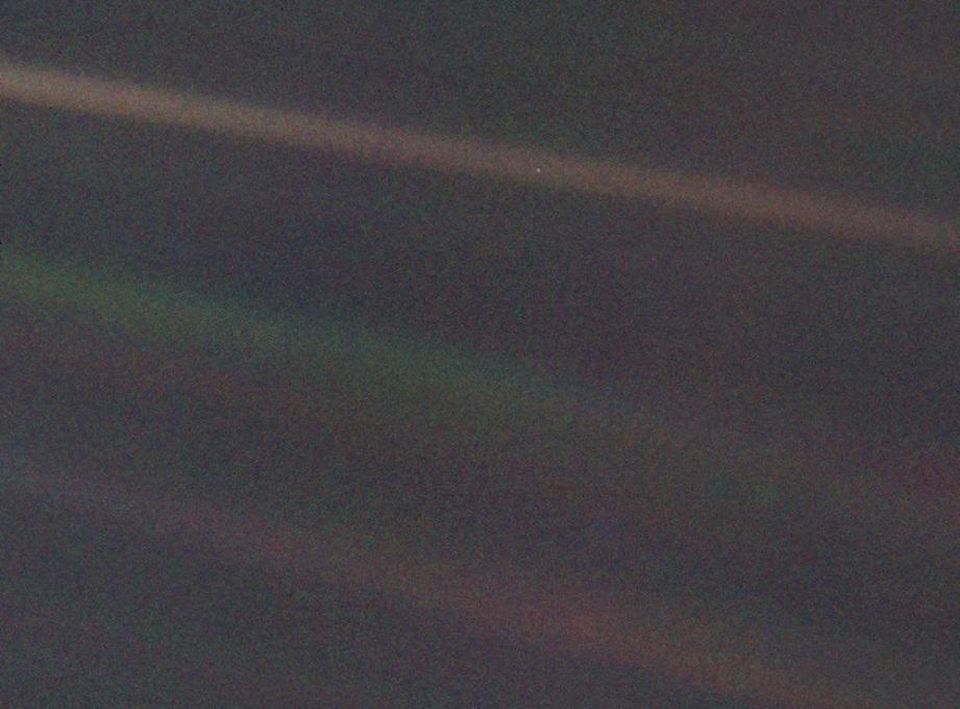 This color image of the Earth, dubbed the “pale blue dot,” is part of the first portrait of the Solar System made by Voyager-1. The spacecraft collected 60 frames for this mosaic depicting the solar system from a distance of more than 6.4 billion km. and from a position 32 ° above the ecliptic. From such a huge distance to Voyager, the Earth appears to be a bright point, less than one pixel in size, even in a narrow-angle camera. The size of the crescent of the earth was only 0.12 pixels.
This color image of the Earth, dubbed the “pale blue dot,” is part of the first portrait of the Solar System made by Voyager-1. The spacecraft collected 60 frames for this mosaic depicting the solar system from a distance of more than 6.4 billion km. and from a position 32 ° above the ecliptic. From such a huge distance to Voyager, the Earth appears to be a bright point, less than one pixel in size, even in a narrow-angle camera. The size of the crescent of the earth was only 0.12 pixels.4) Photos from Voyager "pale blue dot." On February 14, 1990, after more than a decade-long journey away from Earth and on the way from the Solar System, the Voyager-1 spacecraft turned the camera back toward the house. Looking back, he was able to take photos of six planets, including a photo of the Earth from a distance of 6.4 billion km, and this was the furthest photograph of the Earth ever made.
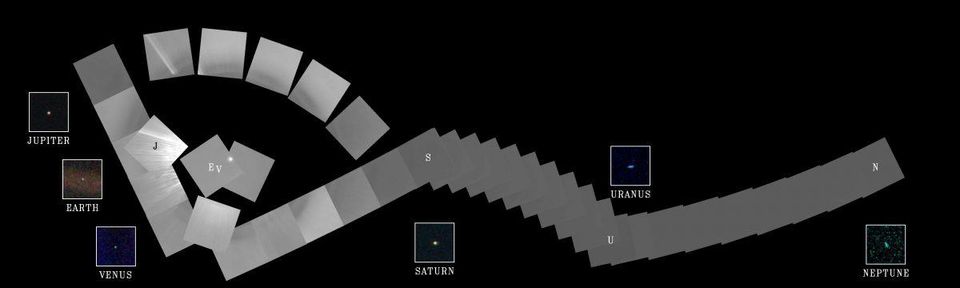 On February 14, 1990, Voyager-1 cameras headed back to the Sun and took a series of photographs of the Sun and planets, creating the first portrait of the Solar System as seen from the outside.
On February 14, 1990, Voyager-1 cameras headed back to the Sun and took a series of photographs of the Sun and planets, creating the first portrait of the Solar System as seen from the outside.And although this image was not part of the original mission plan, the idea of Karl Sagan allowed him to do it, after which he wrote the following:
It's here. This is a house. This is us. Everyone you love lives on it, everyone you know, everyone you've ever heard of, every human being that ever existed has lived its own life. Perhaps there is no better demonstration of imprudent human arrogance than this remote image of our tiny world.
Voyager 1 is now 20 billion km. from us, and continues its journey into interstellar space, remaining the farthest spacecraft sent from Earth.
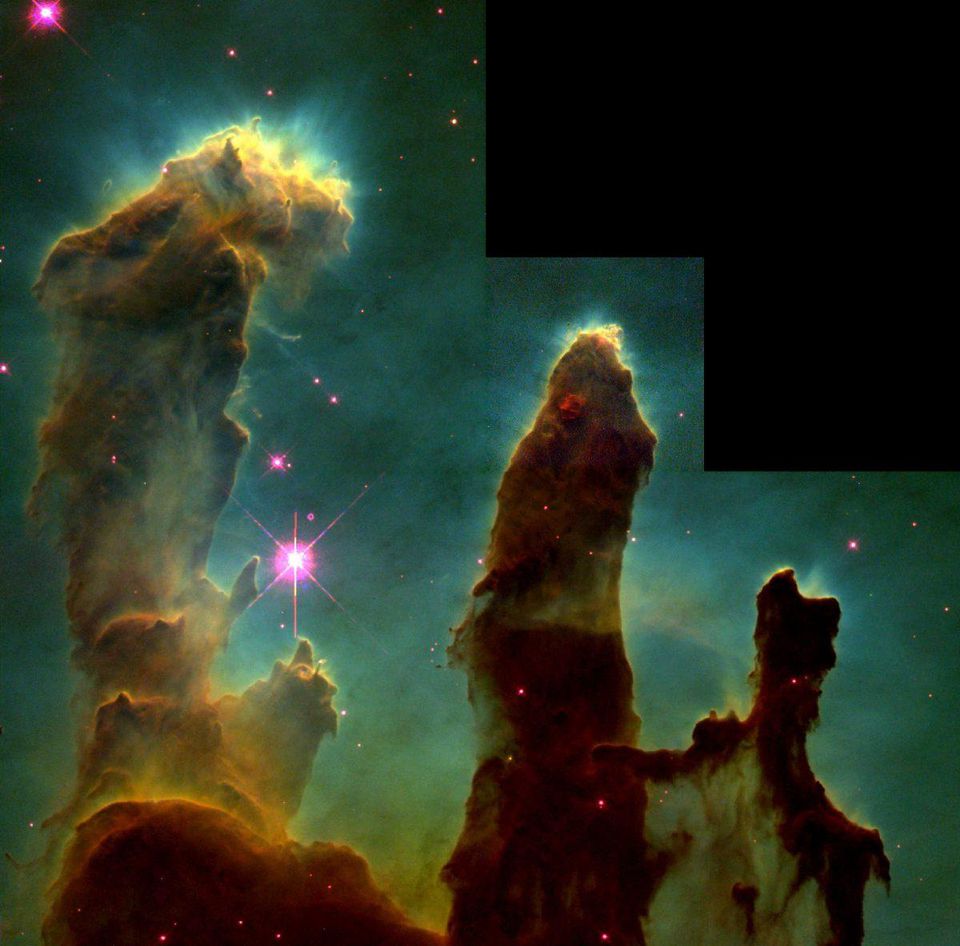 The original image of the “Pillars of Creation” was a mosaic of many different images and filters, but it has already lost its significance compared to more modern data.
The original image of the “Pillars of Creation” was a mosaic of many different images and filters, but it has already lost its significance compared to more modern data.5) Photo Hubble "Pillars of Creation." Many of the visible nebulae located in our galaxy and beyond are regions of active star formation, in which cold molecular gas is compressed under the influence of gravity and creates new stars. In 1995, for the first time, we were able to look into the depth of one such region, into
the Eagle Nebula , and discover the pillars of gas among the stars. They contain protostars, which are still in the process of formation, and these pillars evaporate both from the inside and the outside, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation emitted by hot, newly emerging young stars.
In other words, the "pillars of creation" are also pillars of destruction. In the infrared and X-ray ranges, the stars inside are visible, and the higher resolution version of the image, which appeared 20 years later, showed slow evaporation and changes occurring in the pillars. Over the period from several hundred thousand to several million years, they completely evaporate.
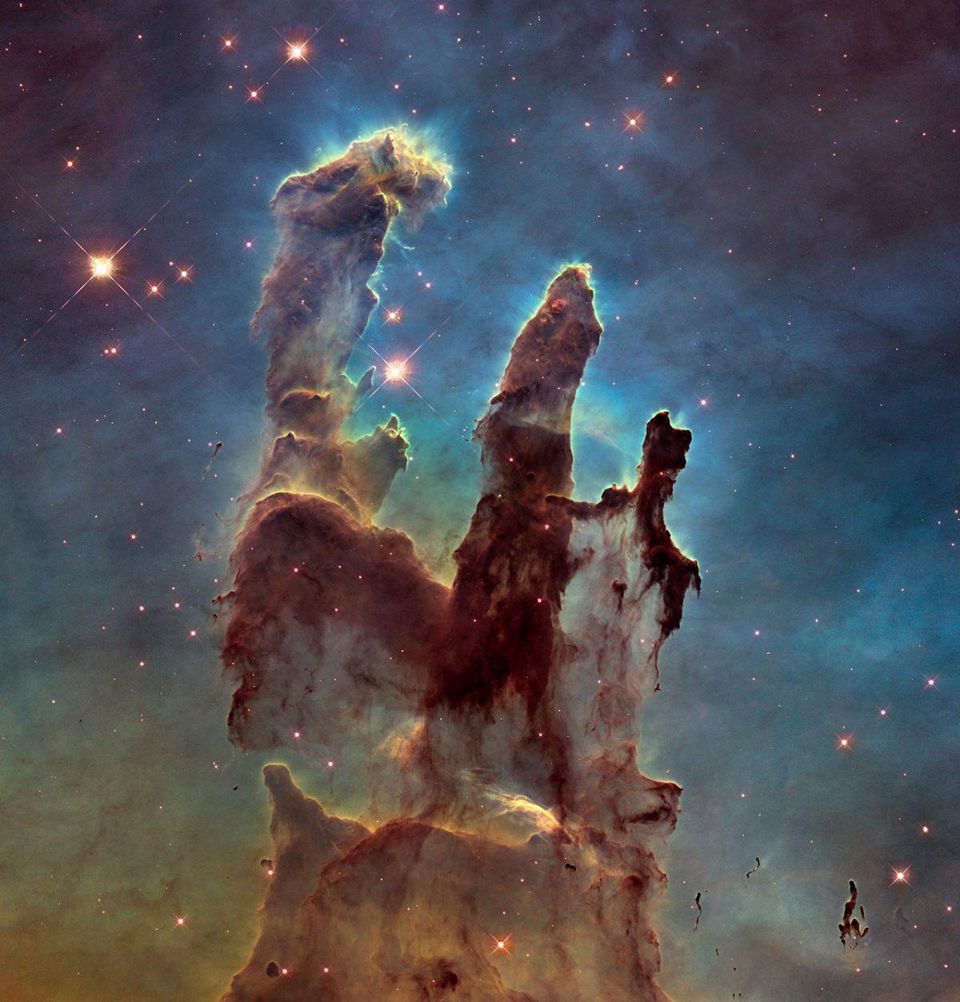 A view of the pillars of creation from 2015 shows a combination of visible and infrared light, a wide viewing angle, spectral lines, indicating the presence of a large variety of heavy elements, and differences from the earlier 1995 image.
A view of the pillars of creation from 2015 shows a combination of visible and infrared light, a wide viewing angle, spectral lines, indicating the presence of a large variety of heavy elements, and differences from the earlier 1995 image.One hundred years ago, we did not even know that in addition to our Milky Way, there were other galaxies in the Universe. We did not know how our Universe appeared, whether it was eternal, how old it was and what it was made of. We had no idea about the fate of the development of the Universe and how long the stars would shine. Today we know the answers to all these questions, and to many others. An investment in space exploration is a worldwide benefit. Studies have shown that these investments depend not only on scientists, but also on all of us, ordinary people. We can study, learn and recognize the Universe as we never dreamed of. And it depends only on us.