Remember how Cryptocics overturned the network of the Ether?
The number of unconfirmed pending transactions broke all records, transaction fees also reached absurd heights, and one user (by mistake) paid commissions of 11 thousand dollars . In this article I would like to talk about what solutions (or hypotheses) are today about increasing the scalability of blockchain projects.
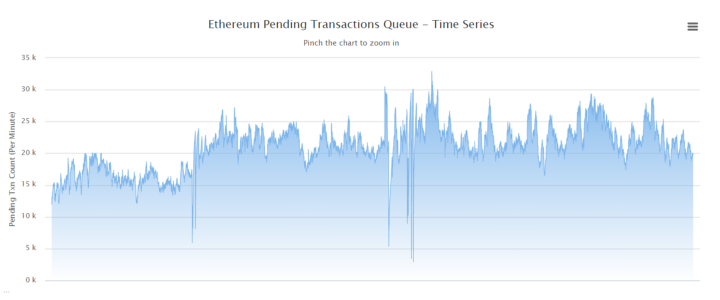
The number of unconfirmed Ethereum transactions from December 5 (Record mark exceeds 30 thousand)
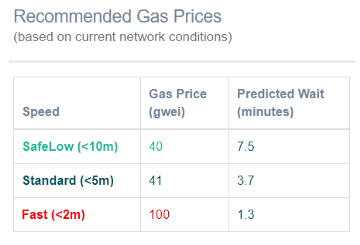
Gas prices, more than 40 Gwei required for confirmation
The need for decisions to scale every day becomes more and more acute, because the commissions and the waiting time of transactions increase.
Devcon3 named several potential scaling solutions that can eliminate, if not all, of most of today's scaling problems. However, these solutions, with the exception of uRaiden, are at the research stage and are not yet sufficiently developed for the main network. Other experts suggest raising the gas limit per block (something like Bitcoin’s block size increase), but this solution also has its drawbacks.
In the meantime, there has been an obvious demand for solutions for scaling that can work today. It is necessary to cope with the needs of existing decentralized applications so as not to completely overload the Ethereum network. Even if such a primitive application as CryptoKitties can put Ethereum out of operation, how can the network cope with a StarCraft application with a million users?
“You could run StarCraft on the blockchain. This is possible. The high level of reliability and scalability allows other various applications to be built on the blockchain. Ethereum is a reliable base layer with a small number of functions ”- Vitalik Buterin
The purpose of this article is to describe how to achieve scaling on Ethereum using specialized sidechains with a customizable “rule set” and at the same time preserve the reliability of the main Ethereum chain.
Scaling with sidechains
The term “sidechain” first appeared in the article
“Innovative features of blockchains that open with sidechain bindings” , published by Adam Beck and co-authors in 2014. The article describes the “bidirectional binding of sidechains”, a mechanism in which you prove that you “blocked” coins that you owned before and that you can move other coins within the sidechain. Here we need to clarify one point to avoid misunderstanding.
Sidechains can scale up but do not imply scalability. Sidechains provide scalability no better than increasing block size. But sidechains allow you to experiment to be able to build networks that run on other technologies — perhaps on technologies with better scaling. ¹
A sidechain is defined by a custom “rule set” and can be used to unload calculations from another chain. Individual sidechains can follow different sets of rules in the main chain, which means that they can be optimized for applications that require extremely high speeds or complex calculations, but still rely on the main chain for matters requiring the highest level of security.
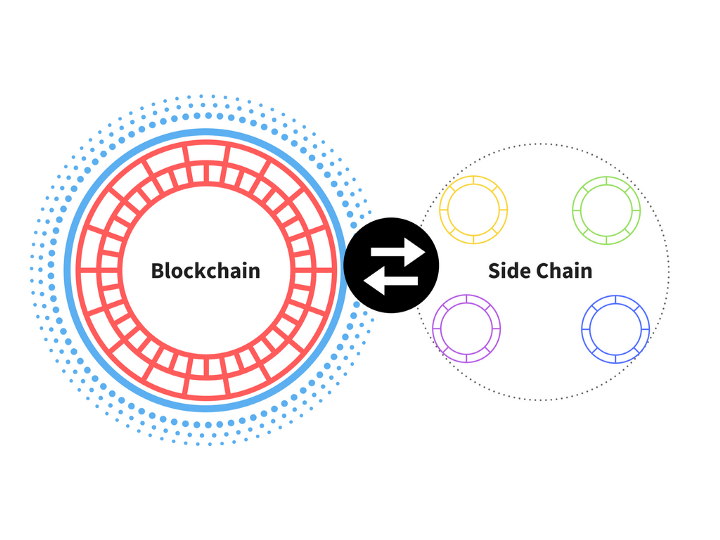
A source
Specialized sidechains
The rules that define sidechain can add privacy or even security and trade decentralization features to increase throughput. Here opens a huge scope for experiments. Depending on the needs of a particular application, you can make settings that will ensure optimum efficiency for it.
Also, incentives in the case of data-driven applications will differ from financial applications. It is possible that the hacker will find it expedient to spend millions of dollars to organize a 51% attack on the financial blockchain and cancel the payment, but he is unlikely to do the same to cancel the tweet on the microblogging platform. Therefore, applications need to be able to choose more flexible threat modeling and work optimization.
There is a huge need for applications that cannot be stopped, which resist censorship, are transparent and work as efficiently as possible.
Thus, in a decentralized Twitter-like application running on the blockchain, adjustable security can provide higher throughput by providing the main chain of “control points” to fix the final version of the information currently available.
We described how to scale decentralized applications. But what will happen if, due to a potential model with a reduced security level, a community becomes so influential that it can control sidechain?
How to achieve independence with hardforks
In centralized communities, such as the sabreddits, sometimes there is a harmful moderator, who begins to edit comments to his own advantage and over time simply destroys the community.
In multiplayer games such as World of Warcraft, global changes are sometimes carried out against the will of the community, and users have no opportunity to argue - either they accept the new rules, or they drop the game. Even Vitalik Buterin was amazed by such events!
“I happily played World of Warcraft from 2007 to 2010, but one day Blizzard removed the damage component from my favorite Warlock Siphon Life spell. I cried until I fell asleep, and then I realized what horrors centralized services are capable of. Soon I threw this game. ”
Coordinated communities should be able to avoid situations that seem unfair to them, and choose an alternative that everyone will agree with.
The key to reaching such agreements is hard forks in sidechains.
If you describe the term as briefly as possible, fork is a mechanism for updating the protocol. In Vitalik's blog you can find a very high-quality comparison of forks.

Venn diagram with forks options, source
Hardfork is a categorical discrepancy with the previous version of the blockchain. Nodes working with the previous version will not accept the new version of the protocol. ¹
How can this achieve independence?
If there is a change that the community does not agree with, then such a community can branch out and continue working in the previous version of sidechain.
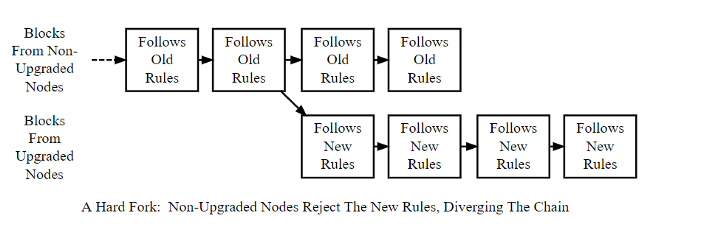
The proposed change, which is not according to the community, can be ignored. The community (represented by the majority of those who disagree) can continue to work in the old chain.
If this happens, say, in a game, many questions will arise:
- What if most of the leading "bad" developers decide to stay in the old chain?
- Will the new chain lag behind or will the developers adapt and compromise?
We do not have all the answers, but believe me, as such self-government applications are created, the free market will figure it out and select the best practices.
At least in this case, the community has a choice.
The Loom Network aims to become a platform where communities run their programs in sidechains, and where everyone is interested in honesty and transparency, and they also want to regulate security restrictions if necessary.
Communities can work on the blockchain, in which users can deploy their own nodes and protect the network. These communities can be networks like Steemit, subreddits, forums, Facebook groups, sites with questions and answers like Stack Overflow - in general, places where people can discuss common interests - as well as multiplayer games where everyone will be interested in fair rules. . If any change is not supported by the community, users should be able to branch off into the fork.
When developers can create such platforms with the same ease with which they create modern Web 2.0 applications, then the blockchain revolution will begin.